RHOA and mDia1 Promotes Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells Via a High Dose of Doxorubicin Treatment
- PMID: 33817200
- PMCID: PMC7874778
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2019-0070
RHOA and mDia1 Promotes Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells Via a High Dose of Doxorubicin Treatment
Abstract
Background: Transforming RhoA proteins (RHOA) and their downstream Diaphanous homolog 1 proteins (DIAPH1) or mDia1 participate in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton which plays critical role in cells, i.e., morphologic changes and apoptosis.
Methodology: To determine the cell viability the real time cell analysis (RTCA) and flow cytometry were used. To perform proteomic analysis, the label-free quantitative method and post-translation modification by the nano-HPLC and ESI-MS ion trap mass analyser were used.
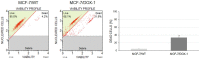
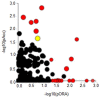
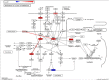
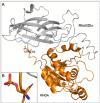
Results: The results of the cell viability showed an increase of dead cells (around 30 %) in MCF-7/DOX-1 (i.e., 1μM of doxorubicin was added to MCF-7/WT breast cancer cell line) compared to MCF-7/WT (control) after 24 h doxorubicin (DOX) treatment. The signalling pathway of the Regulation of actin cytoskeleton (p<0.0026) was determined, where RHOA and mDia1 proteins were up-regulated. Also, post-translational modification analysis of these proteins in MCF-7/DOX-1 cells revealed dysregulation of the actin cytoskeleton, specifically the collapse of actin stress fibbers due to phosphorylation of RHOA at serine 188 and mDia1 at serine 22, resulting in their deactivation and cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: These results pointed to an assumed role of DOX to dysregulation of actin cytoskeleton and cell death.
Keywords: Diaphanous homolog 1 protein; Transforming RhoA protein; actin cytoskeleton; stress fibre.
© 2019 Peter Bober et al. published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ng R, Better N, Green MD. Anticancer Agents and Cardiotoxicity. Semin Oncol. 2006;33:2–14. - PubMed
-
- Sereno M, Brunello A, Chiappori A, Barriuso J, Casado E, Belda C. Cardiac toxicity: Old and new issues in anti-cancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 2008;10:35–46. et al. - PubMed
-
- Schimmel KJM, Richel DJ, van den Brink RBA, Guchelaar HJ. Cardiotoxicity of cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004;30:181–191. - PubMed
-
- Tacar O, Sriamornsak P, Dass CR. Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013;65:157–170. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
