Age in relation to comorbidity and outcome in patients with high-risk TIA or minor ischemic stroke: A Swedish national observational study
- PMID: 33817335
- PMCID: PMC7995324
- DOI: 10.1177/2396987320975980
Age in relation to comorbidity and outcome in patients with high-risk TIA or minor ischemic stroke: A Swedish national observational study
Abstract
Introduction: Recent trials report positive results for preventing vascular events with dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) in patients with high-risk TIA or minor ischemic stroke. We aimed to investigate this population regarding influence of age on vascular risk factors, hospital stay and mortality.
Patients and methods: Data on patients aged 40-100 years with TIA or ischemic stroke in the Swedish Stroke Register during 2012-13 were linked with national registers. To identify patients with high-risk TIA (ABCD2 ≥6) or minor ischemic stroke (NIHSS ≤5) eligible for DAPT, we excluded patients with atrial fibrillation, anticoagulant use, prior major bleeding, or unknown stroke severity.
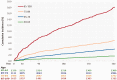
Findings: We identified 10,053 potential DAPT-candidates (mean age 72.6 years, 45.2% female, 16.4% with TIA). With advancing age, most vascular risk factors increased. Antiplatelet treatment increased from 31.9% before the event to 95.5% after discharge. Within 1 year following index event, the proportion of patients with ≥1 re-admission increased with age (29.2% in 40-64 year-olds; 47.2% in 85-100 year-olds). All-cause death per 100 person-years was 6.9 (95% CI 6.4-7.4) within 1 year, and highest in the first 30 days (15.2; 95% CI 12.8-18.2). For each year of increased age, the risk of death increased with 3.5% (p = 0.128) in patients 40-64 years and with 11.8% (p < 0.001) in those ≥85 years.
Conclusions: While in theory representing a subset of patients with mild injury, our observational study highlights substantial use of health-care resources and high mortality rates among patients with high-risk TIA or minor ischemic stroke assumed eligible for DAPT.
Keywords: Ischemic attack; epidemiology; ischemic stroke; mortality; mortality/survival; platelet aggregation inhibitors; registries; secondary prevention; stroke; transient; transient ischemic attack (TIA).
© European Stroke Organisation 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: BF, OF, and PA declare no conflicts of interest in relation to this study; JH, PL, EL, and CM are employees of AstraZeneca; SÅ has received institutional research funding from AstraZeneca.
Figures
References
-
- Feigin VL, Lawes CMM, Bennett DA, et al.. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8: 355–369. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Halpern M, Meier N, et al.. Age-dependent differences in demographics, risk factors, co-morbidity, etiology, management, and clinical outcome of acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol 2008; 255: 1503–1507. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources