Pulmonary function and COVID-19
- PMID: 33817453
- PMCID: PMC7997144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cophys.2021.03.005
Pulmonary function and COVID-19
Abstract
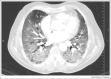
In people recovering from COVID-19, there is concern regarding potential long-term pulmonary sequelae and associated impairment of functional capacity. Data published thus far indicate that spirometric indices appear to be generally well preserved, but that a defect in diffusing capacity (DLco) is a prevalent abnormality identified on follow-up lung function; present in 20-30% of those with mild to moderate disease and 60% in those with severe disease. Reductions in total lung capacity were commonly reported. Functional capacity is also often impaired, with data now starting to emerge detailing walk test and cardiopulmonary exercise test outcome at follow-up. In this review, we evaluate the published evidence in this area, to summarise the impact of COVID-19 infection on pulmonary function and relate this to the clinico-radiological findings and disease severity.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation . WHO; 2020. Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pp. 1–9. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/who-convened-global-study-of-the....
-
- Bernheim A., Mei X., Huang M., Yang Y., Fayad Z.A., Zhang N., et al. Chest CT findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): relationship to duration of infection. Radiology. 2020;295 Available from: http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.2020200463. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai H.X., Hsieh B., Xiong Z., Halsey K., Choi J.W., Tran T.M.L., et al. Performance of radiologists in differentiating COVID-19 from non-COVID-19 viral pneumonia at chest CT. Radiology. 2020;296:E46–E54. Available from: http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.2020200823. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Provencher S., Potus F., Bonnet S. COVID-19 and the pulmonary vasculature. Pulm Circ. 2020;10 Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/2045894020933088. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sonnweber T., Sahanic S., Pizzini A., Luger A., Schwabl C., Sonnweber B., et al. Cardiopulmonary recovery after COVID-19 – an observational prospective multi-center trial. Eur Respir J. 2020;57 Available from: http://erj.ersjournals.com/lookup/doi/10.1183/13993003.03481-2020. - PMC - PubMed
-
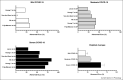
Prospective multi-centre observational study with PFT measurements at 60 and 100 days after COVID-19 onset. Total abnormality at visit 1 was 42% and at visit 2 was 36%. DLco was <80% predicted in 31% at visit 1 and 21% at visit 2 suggesting an improvement with convalescence.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
