Seasonal and daytime variation in multiple immune parameters in humans: Evidence from 329,261 participants of the UK Biobank cohort
- PMID: 33817568
- PMCID: PMC8010467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102255
Seasonal and daytime variation in multiple immune parameters in humans: Evidence from 329,261 participants of the UK Biobank cohort
Abstract
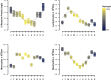
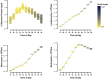
Seasonal disease outbreaks are perennial features of human infectious disease but the factors generating these patterns are unclear. Here we investigate seasonal and daytime variability in multiple immune parameters in 329,261 participants in UK Biobank and test for associations with a wide range of environmental and lifestyle factors, including changes in day length, outdoor temperature and vitamin D at the time the blood sample was collected. Seasonal patterns were evident in lymphocyte and neutrophil counts, and C-reactive protein CRP, but not monocytes, and these were independent of lifestyle, demographic, and environmental factors. All the immune parameters assessed demonstrated significant daytime variation that was independent of confounding factors. At a population level, human immune parameters vary across season and across time of day, independent of multiple confounding factors. Both season and time of day are fundamental dimensions of immune function that should be considered in all studies of immuno-prophylaxis and disease transmission.
Keywords: Chronobiology; Immune Response; Immunology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Population-level seasonality in cardiovascular mortality, blood pressure, BMI and inflammatory cells in UK biobank.Ann Med. 2018 Aug;50(5):410-419. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2018.1472389. Epub 2018 May 18. Ann Med. 2018. PMID: 29724143
-
Seasonality of depressive symptoms in women but not in men: A cross-sectional study in the UK Biobank cohort.J Affect Disord. 2018 Mar 15;229:296-305. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.12.106. Epub 2018 Jan 4. J Affect Disord. 2018. PMID: 29329063
-
Tapping natures rhythm: the role of season in mitochondrial function and genetics in the UK biobank.Hum Genomics. 2025 Mar 29;19(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40246-025-00743-8. Hum Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40158147 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal Heat Acclimatisation in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review.Sports Med. 2022 Sep;52(9):2111-2128. doi: 10.1007/s40279-022-01677-0. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 35460514 Free PMC article.
-
The role of UV radiation and vitamin D in the seasonality and outcomes of infectious disease.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2017 Mar 16;16(3):314-338. doi: 10.1039/c6pp00355a. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28078341 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles for Pathogen Interference in Influenza Vaccination, with Implications to Vaccine Effectiveness (VE) and Attribution of Influenza Deaths.Infect Dis Rep. 2022 Sep 23;14(5):710-758. doi: 10.3390/idr14050076. Infect Dis Rep. 2022. PMID: 36286197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian immunity from bench to bedside: a practical guide.J Clin Invest. 2024 Feb 1;134(3):e175706. doi: 10.1172/JCI175706. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38299593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
White blood cells in pregnancy: reference intervals for before and after delivery.EBioMedicine. 2021 Dec;74:103715. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103715. Epub 2021 Nov 23. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34826802 Free PMC article.
-
Population-wide analysis of hospital laboratory tests to assess seasonal variation and temporal reference interval modification.Patterns (N Y). 2023 Jun 28;4(8):100778. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100778. eCollection 2023 Aug 11. Patterns (N Y). 2023. PMID: 37602220 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Effects on Vascular Immunopathologies.Circ Res. 2024 Mar 15;134(6):791-809. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323619. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Circ Res. 2024. PMID: 38484032 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abo T., Kawate T., Itoh K., Kumagai K. Studies on the bioperiodicity of the immune response. I. Circadian rhythms of human T, B, and K cell traffic in the peripheral blood. J. Immunol. 1981;126:1360–1363. - PubMed
-
- Adrover J.M., del Fresno C., Crainiciuc G., Cuartero M.I., Casanova-Acebes M., Weiss L.A., Huerga-Encabo H., Silvestre-Roig C., Rossaint J., Cossío I. A neutrophil timer coordinates immune defense and vascular protection. Immunity. 2019;50:390–402.e10. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

