Deletion of renal Nedd4-2 abolishes the effect of high sodium intake (HS) on Kir4.1, ENaC, and NCC and causes hypokalemia during high HS
- PMID: 33818128
- PMCID: PMC8174810
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00555.2020
Deletion of renal Nedd4-2 abolishes the effect of high sodium intake (HS) on Kir4.1, ENaC, and NCC and causes hypokalemia during high HS
Abstract
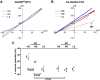
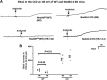
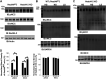
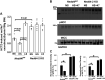
Neural precursor cell expressed developmentally downregulated protein 4-2 (Nedd4-2) regulates the expression of Kir4.1, thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter (NCC), and epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) in the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron (ASDN), and Nedd4-2 deletion causes salt-sensitive hypertension. We now examined whether Nedd4-2 deletion compromises the effect of high-salt (HS) diet on Kir4.1, NCC, ENaC, and renal K+ excretion. Immunoblot analysis showed that HS diet decreased the expression of Kir4.1, Ca2+-activated large-conductance K+ channel subunit-α (BKα), ENaCβ, ENaCγ, total NCC, and phospho-NCC (at Thr53) in floxed neural precursor cell expressed developmentally downregulated gene 4-like (Nedd4lfl/fl) mice, whereas these effects were absent in kidney-specific Nedd4-2 knockout (Ks-Nedd4-2 KO) mice. Renal clearance experiments also demonstrated that Nedd4-2 deletion abolished the inhibitory effect of HS diet on hydrochlorothiazide-induced natriuresis. Patch-clamp experiments showed that neither HS diet nor low-salt diet had an effect on Kir4.1/Kir5.1 currents of the distal convoluted tubule in Nedd4-2-deficient mice, whereas we confirmed that HS diet inhibited and low-salt diet increased Kir4.1/Kir5.1 activity in Nedd4lflox/flox mice. Nedd4-2 deletion increased ENaC currents in the ASDN, and this increase was more robust in the cortical collecting duct than in the distal convoluted tubule. Also, HS-induced inhibition of ENaC currents in the ASDN was absent in Nedd4-2-deficient mice. Renal clearance experiments showed that HS intake for 2 wk increased the basal level of renal K+ excretion and caused hypokalemia in Ks-Nedd4-2-KO mice but not in Nedd4lflox/flox mice. In contrast, plasma Na+ concentrations were similar in Nedd4lflox/flox and Ks-Nedd4-2 KO mice on HS diet. We conclude that Nedd4-2 plays an important role in mediating the inhibitory effect of HS diet on Kir4.1, ENaC, and NCC and is essential for maintaining normal renal K+ excretion and plasma K+ ranges during long-term HS diet.NEW & NOTEWORTHY The present study suggests that Nedd4-2 is involved in mediating the inhibitory effect of high salt (HS) diet on Kir4.1/kir5.1 in the distal convoluted tubule, NaCl cotransporter function, and epithelial Na+ channel activity and that Nedd4-2 plays an essential role in maintaining K+ homeostasis in response to a long-term HS diet. This suggests the possibility that HS intake could lead to hypokalemia in subjects lacking proper Nedd4-2 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity in aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron.
Keywords: Kir4.1/Kir5.1; collecting duct; distal convoluted tubule; renal K+ excretion.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Deletion of renal Nedd4-2 abolishes the effect of high K+ intake on Kir4.1/Kir5.1 and NCC activity in the distal convoluted tubule.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):F1-F11. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00072.2021. Epub 2021 May 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34029145 Free PMC article.
-
ROMK channels are inhibited in the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron of renal tubule Nedd4-2-deficient mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Jan 1;322(1):F55-F67. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00306.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34843409 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Kir5.1 abolishes the effect of high Na+ intake on Kir4.1 and Na+-Cl- cotransporter.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 Jun 1;320(6):F1045-F1058. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00004.2021. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33900854 Free PMC article.
-
Role of inwardly rectifying K+ channel 5.1 (Kir5.1) in the regulation of renal membrane transport.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2022 Sep 1;31(5):479-485. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000817. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35894283 Review.
-
Basolateral Kir4.1 activity in the distal convoluted tubule regulates K secretion by determining NaCl cotransporter activity.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Sep;25(5):429-35. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000248. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27306796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EAST/SeSAME Syndrome and Beyond: The Spectrum of Kir4.1- and Kir5.1-Associated Channelopathies.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 15;13:852674. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.852674. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35370765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldosterone: Renal Action and Physiological Effects.Compr Physiol. 2023 Mar 30;13(2):4409-4491. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c190043. Compr Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36994769 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of renal Nedd4-2 abolishes the effect of high K+ intake on Kir4.1/Kir5.1 and NCC activity in the distal convoluted tubule.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):F1-F11. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00072.2021. Epub 2021 May 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34029145 Free PMC article.
-
ROMK channels are inhibited in the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron of renal tubule Nedd4-2-deficient mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Jan 1;322(1):F55-F67. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00306.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34843409 Free PMC article.
-
Control of sodium and potassium homeostasis by renal distal convoluted tubules.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023 Feb 10;56:e12392. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2023e12392. eCollection 2023. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 36790288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arroyo JP, Lagnaz D, Ronzaud C, Vazquez N, Ko BS, Moddes L, Ruffieux-Daidie D, Hausel P, Koesters R, Yang B, Stokes JB, Hoover RS, Gamba G, Staub O. Nedd4-2 modulates renal Na+-Cl− cotransporter via the aldosterone-SGK1-Nedd4-2 pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol 22: 1707–1719, 2011. doi:10.1681/asn.2011020132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Debonneville C, Flores SY, Kamynina E, Plant PJ, Tauxe C, Thomas MA, Munster C, Chraibi A, Pratt JH, Horisberger JD, Pearce D, Loffing J, Staub O. Phosphorylation of Nedd4-2 by Sgk1 regulates epithelial Na+ channel cell surface expression. EMBO J 20: 7052–7059, 2001. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.24.7052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ronzaud C, Loffing-Cueni D, Hausel P, Debonneville A, Malsure SR, Fowler-Jaeger N, Boase NA, Perrier R, Maillard M, Yang B, Stokes JB, Koesters R, Kumar S, Hummler E, Loffing J, Staub O. Renal tubular NEDD4-2 deficiency causes NCC-mediated salt-dependent hypertension. J Clin Invest 123: 657–665, 2013. doi:10.1172/jci61110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

