Diagnostic accuracy of the cancer ratio for the prediction of malignant pleural effusion: evidence from a validation study and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33818231
- PMCID: PMC8023604
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1906943
Diagnostic accuracy of the cancer ratio for the prediction of malignant pleural effusion: evidence from a validation study and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the diagnostic accuracy of serum LDH to pleural ADA ratio (cancer ratio, CR)for malignant pleural effusion (MPE) through an original study and meta-analysis.
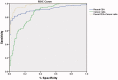
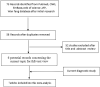
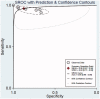
Methods: We retrospectively collected data from 145 patients with MPE and 117 cases of benign pleural effusions (BPE). The diagnostic performance of CR and a typical biomarker of MPE, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), were analysed using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and the area under the curve (AUC) as a measure of accuracy. The overall diagnostic accuracy of CR was summarised by a standard diagnostic meta-analysis.
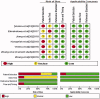
Results: Significantly higher CR and pleural CEA values were observed in the MPE patients than in the BPE patients. At a cut-off value of 14.97, CR showed high sensitivity (0.91), low specificity (0.67), and high AUC (0.85). The combination of CEA and CR increased the AUC to 0.98. The meta-analysis included seven studies involving 2,078 patients. The pooled values for sensitivity, specificity, positive/negative likelihood ratio, and diagnostic odds ratio of CR were 0.96, 0.88, 7.70, 0.05, and 169, respectively. The AUC of the summary ROC of CR was 0.98.
Conclusion: CR has a high diagnostic accuracy for predicting MPE, especially when used in combination with pleural CEA.
Keywords: Malignant pleural effusion; cancer ratio; carcinoembryonic antigen; diagnosis; meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Meriggi F. Malignant pleural effusion: still a long way to go. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2019; 14(1):24–30. - PubMed
-
- Thomas JM, Musani AI.. Malignant pleural effusions: a review. Clin Chest Med. 2013;34(3):459–471. - PubMed
-
- Egan AM, McPhillips D, Sarkar S, et al. Malignant pleural effusion. QJM. 2014;107(3):179–184. - PubMed
-
- Montero-Arias F, Cartin-Ceba R, Rojas-Solano J, et al. Pleural effusion size as prognostic marker in patients with malignant pleural effusion. Pleura. 2015;2:237399751560065.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
