Down-regulation of miR-340-5p promoted osteogenic differentiation through regulation of runt-related transcription factor-2 (RUNX2) in MC3T3-E1 cells
- PMID: 33818278
- PMCID: PMC8291863
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1905259
Down-regulation of miR-340-5p promoted osteogenic differentiation through regulation of runt-related transcription factor-2 (RUNX2) in MC3T3-E1 cells
Abstract
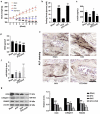
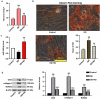
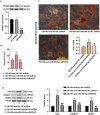
Diabetic osteoporosis (DOP) is a chronic complication of diabetes in the skeletal system. High level of miR-340-5p may be harmful to the bone formation. In this study, the DOP model of rats was successfully established via streptozotocin (STZ) and ovariectomy (OVX) treatment. It was manifested by reduced body weight, insulin level, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, and osteocalcin (OCN) and collagen-I expressions, as well as increased concentration of fasting blood glucose. Moreover, we found that miR-340-5p expression was increased while runt-related transcription factor-2 (RUNX2) was decreased in femurs. Furthermore, the effects of miR-340-5p on osteogenic differentiation (OD) in high glucose (HG)-treated MC3T3-E1 cells were explored. Exposure to OD and HG contributed to elevated miR-340-5p level. Inhibition of miR-340-5p enhanced ALP level, calcium deposition, and OCN, collagen-I and RUNX2 levels. On the contrary, miR-340-5p overexpression reversed these promotional effects. Luciferase assay indicated that RUNX2 may be a target gene of miR-340-5p. Moreover, RUNX2 deficiency decreased miR-340-5p inhibition-induced ALP activity, calcium accumulation and OCN, collagen-I, RUNX2 levels. In short, the above findings revealed that inhibition of miR-340-5p facilitated osteogenic differentiation through regulating RUNX2 in MC3TC-E1 cells, which provided targeted therapeutic strategies for the treatment of DOP.
Keywords: Mir-340-5p; mc3t3-e1 cells; osteogenic differentiation; runx2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Gong K, Qu B, Liao D, et al. MiR-132 regulates osteogenic differentiation via downregulating Sirtuin1 in a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β/δ-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478(1):260–267. - PubMed
-
- Inzerillo AM, Epstein S.. Osteoporosis and diabetes mellitus. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2004;5(3):261–268. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Chen X, Chen B, et al. Tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside protected against diabetes-induced osteoporosis in mice with streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Phytother Res. 2019;33(2):442–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
