Teriflunomide provides protective properties after oxygen-glucose-deprivation in hippocampal and cerebellar slice cultures
- PMID: 33818508
- PMCID: PMC8354112
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.310689
Teriflunomide provides protective properties after oxygen-glucose-deprivation in hippocampal and cerebellar slice cultures
Abstract
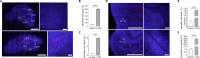
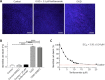
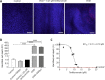
One of the major challenges in emergency medicine is out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). Every year, about 53-62/100 000 people worldwide suffer an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with serious consequences, whereas persistent brain injury is a major cause of morbidity and mortality of those surviving a cardiac arrest. Today, only few and insufficient strategies are known to limit neurological damage of ischemia and reperfusion injury. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether teriflunomide, an approved drug for treatment of relapsing-remitting-multiple-sclerosis, exerts a protective effect on brain cells in an in vitro model of ischemia. Therefore, organotypic slice cultures from rat hippocampus and cerebellum were exposed to oxygen-glucose-deprivation and subsequently treated with teriflunomide. The administration of teriflunomide in the reperfusion time on both hippocampal and cerebellar slice cultures significantly decreased the amount of detectable propidium iodide signal compared with an untreated culture, indicating that more cells survive after oxygen-glucose-deprivation. However, hippocampal slice cultures showed a higher vulnerability to ischemic conditions and a more sensitive response to teriflunomide compared with cerebellar slice cultures. Our study suggests that teriflunomide, applied as a post-treatment after an oxygen-glucose-deprivation, has a protective effect on hippocampal and cerebellar cells in organotypic slice cultures of rats. All procedures were conducted under established standards of the German federal state of North Rhine Westphalia, in accordance with the European Communities Council Directive 2010/63/EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes.
Keywords: brain damage; cardiac arrest; cell death; hypoxic chamber; ischemia; organotypic slice cultures; post-treatment; resuscitation.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Region-specific protective effects of monomethyl fumarate in cerebellar and hippocampal organotypic slice cultures following oxygen-glucose deprivation.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 7;19(8):e0308635. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308635. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39110748 Free PMC article.
-
Ionotropic glutamate receptors and glutamate transporters are involved in necrotic neuronal cell death induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation of hippocampal slice cultures.Neuroscience. 2005;136(3):779-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.07.020. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 16344151
-
Methods to induce primary and secondary traumatic damage in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures.Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 2000 Apr;5(2):153-8. doi: 10.1016/s1385-299x(00)00007-6. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 2000. PMID: 10775835
-
Organotypic hippocampal slice cultures for studies of brain damage, neuroprotection and neurorepair.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2005 Aug;4(4):435-52. doi: 10.2174/1568007054546108. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2005. PMID: 16101559 Review.
-
Organotypic cultures of cerebellar slices as a model to investigate demyelinating disorders.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017 Oct;12(10):1011-1022. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2017.1356285. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28712329 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Protective Effects of Edaravone in Cerebellar and Hippocampal Ischemic Injury Models.Cerebellum. 2025 Feb 18;24(2):49. doi: 10.1007/s12311-025-01804-3. Cerebellum. 2025. PMID: 39964549 Free PMC article.
-
Region-specific protective effects of monomethyl fumarate in cerebellar and hippocampal organotypic slice cultures following oxygen-glucose deprivation.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 7;19(8):e0308635. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308635. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39110748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bar-Or A. Teriflunomide (Aubagio®) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Exp Neurol. 2014;262:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Berdowski J, Berg RA, Tijssen JGP, Koster RW. Global incidences of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and survival rates: Systematic review of 67 prospective studies. Resuscitation. 2010;81:1479–1487. - PubMed
-
- Bernard SA, Gray TW, Buist MD, Jones BM, Silvester W, Gutteridge G, Smith K. Treatment of comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with induced hypothermia. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:557–563. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

