Role of Bempedoic Acid in Clinical Practice
- PMID: 33818688
- PMCID: PMC8266788
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-021-07147-5
Role of Bempedoic Acid in Clinical Practice
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Role of Bempedoic Acid in Clinical Practice.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021 Aug;35(4):865. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07188-w. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021. PMID: 33871715 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
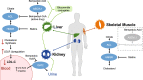
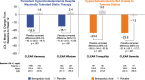
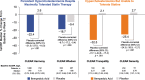
Many patients do not achieve optimal low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels with statins alone; others are unable to tolerate statin therapy. Additional non-statin treatment options including ezetimibe, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors, and bile acid sequestrants are often necessary to further reduce the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. This review provides practical guidance as to the use of bempedoic acid to lower LDL-C and includes direction as to which patients may benefit and advice for safety monitoring during treatment. Bempedoic acid, a new class of agent, is a prodrug converted to bempedoyl-CoA by very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1, an enzyme with high expression in the liver but that is undetectable in the skeletal muscle. Bempedoic acid inhibits the enzyme adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-citrate lyase, which lies two steps upstream from β-hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. In clinical trials conducted in patients with or at risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or familial heterozygous hypercholesterolemia, bempedoic acid in combination with statins and/or ezetimibe significantly reduced LDL-C, apolipoprotein B, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein compared with placebo. Bempedoic acid is generally well tolerated with no clinically meaningful increase in muscle-related symptoms relative to placebo, even in patients taking maximally tolerated statins. A small increase in serum uric acid (mean increase 0.8 mg/dL) is the most noteworthy adverse effect. Bempedoic acid provides an effective and generally well-tolerated medication to further reduce LDL-C in patients taking maximally tolerated statins or manage LDL-C levels in those who are unable to take statins. The potential for a reduced incidence of major cardiovascular events with bempedoic acid is being investigated in the CLEAR Outcomes trial, with results expected in 2023.
Keywords: ATP-citrate lyase; Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; Bempedoic acid; High-sensitivity C-reactive protein; Hypercholesterolemia; Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Conflict of interest statement
CM Ballantyne has received research grant(s)/support paid to his institution from Abbott Diagnostic, Akcea, Amarin, Amgen, Esperion, Ionis, Novartis, Regeneron, Roche Diagnostic, Sanofi-Synthelabo, NIH, AHA, and ADA. He has also served as a consultant for Abbott Diagnostics, Amarin, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Intercept, Ionis, Matinas BioPharma Inc., Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Regeneron, Roche Diagnostic, and Sanofi-Synthelabo.
H Bays’ research site has received research grants from 89Bio, Acasti, Akcea, Allergan, Alon Medtech/Epitomee, Amarin, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Axsome, Boehringer Ingelheim, Civi, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Evidera, Gan and Lee, Home Access, Janssen, Johnson and Johnson, Lexicon, Matinas, Merck, Metavant, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Selecta, TIMI, and Urovant. In the past 12 months, he has served as a consultant and/or advisor for 89Bio, Amarin, Esperion, Matinas, and Gelesis and speaker for Esperion.
AL Catapano has received research grant(s)/support from Amgen, Mylan, Menarini, Sanofi, and Sanofi/Regeneron (all paid to the institution, not to the individual) and has served as a consultant for or received honoraria from Akcea, Amgen, Daiichi Sankyo, Esperion, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Kowa, Medco, Menarini, MSD, Mylan, Novartis, Recordati, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A Goldberg has received research grant(s)/support from Amarin, Amgen, Ionis/Akcea, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi and served as a consultant for 23andMe, Akcea, Esperion, Merck, Novartis, OptumRX, Regeneron, and Sanofi/Regeneron.
KK Ray has received research grant(s)/support from Amgen, Daiichi Sankyo, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi (all paid to the institution, not to the individual) and served as a consultant for or received honoraria from Abbott, AbbVie, Akcea, Algorithm, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cerenis, Cipla, Daiichi Sankyo, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Kowa, Lupin, Medco, MSD, New Amsterdam Pharma, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Regeneron, Resverlogix, Sanofi, Silence Therapeutics, Takeda, and Zuellig Pharma.
JJ Saseen declares he has no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Buck G, Pollicino C, et al. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet. 2005;366:1267–1278. - PubMed
-
- Wong ND, Young D, Zhao Y, Nguyen H, Caballes J, Khan I, Sanchez RJ. Prevalence of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association statin eligibility groups, statin use, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol control in US adults using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2012. J Clin Lipidol. 2016;10:1109–1118. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, Braun LT, de Ferranti S, Faiella-Tommasino J, Forman DE, Goldberg R, Heidenreich PA, Hlatky MA, Jones DW, Lloyd-Jones D, Lopez-Pajares N, Ndumele CE, Orringer CE, Peralta CA, Saseen JJ, Smith SC, Jr, Sperling L, Virani SS, Yeboah J. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:e285–e350. - PubMed
-
- Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, Chapman MJ, de Backer GG, Delgado V, Ference BA, Graham IM, Halliday A, Landmesser U, Mihaylova B, Pedersen TR, Riccardi G, Richter DJ, Sabatine MS, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Wiklund O, ESC Scientific Document Group. Mueller C, Drexel H, Aboyans V, Corsini A, Doehner W, Farnier M, Gigante B, Kayikcioglu M, Krstacic G, Lambrinou E, Lewis BS, Masip J, Moulin P, Petersen S, Petronio AS, Piepoli MF, Pintó X, Räber L, Ray KK, Reiner Ž, Riesen WF, Roffi M, Schmid JP, Shlyakhto E, Simpson IA, Stroes E, Sudano I, Tselepis AD, Viigimaa M, Vindis C, Vonbank A, Vrablik M, Vrsalovic M, Zamorano JL, Collet JP, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, John Chapman M, de Backer GG, Delgado V, Ference BA, Graham IM, Halliday A, Landmesser U, Mihaylova B, Pedersen TR, Riccardi G, Richter DJ, Sabatine MS, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Wiklund O, Windecker S, Aboyans V, Baigent C, Collet JP, Dean V, Delgado V, Fitzsimons D, Gale CP, Grobbee D, Halvorsen S, Hindricks G, Iung B, Jüni P, Katus HA, Landmesser U, Leclercq C, Lettino M, Lewis BS, Merkely B, Mueller C, Petersen S, Petronio AS, Richter DJ, Roffi M, Shlyakhto E, Simpson IA, Sousa-Uva M, Touyz RM, Nibouche D, Zelveian PH, Siostrzonek P, Najafov R, van de Borne P, Pojskic B, Postadzhiyan A, Kypris L, Špinar J, Larsen ML, Eldin HS, Viigimaa M, Strandberg TE, Ferrières J, Agladze R, Laufs U, Rallidis L, Bajnok L, Gudjónsson T, Maher V, Henkin Y, Gulizia MM, Mussagaliyeva A, Bajraktari G, Kerimkulova A, Latkovskis G, Hamoui O, Slapikas R, Visser L, Dingli P, Ivanov V, Boskovic A, Nazzi M, Visseren F, Mitevska I, Retterstøl K, Jankowski P, Fontes-Carvalho R, Gaita D, Ezhov M, Foscoli M, Giga V, Pella D, Fras Z, de Isla LP, Hagström E, Lehmann R, Abid L, Ozdogan O, Mitchenko O, Patel RS. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:111–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

