Conditional survival and hazards of death for peripheral T-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 33819191
- PMCID: PMC8064157
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202782
Conditional survival and hazards of death for peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Abstract
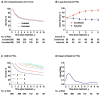
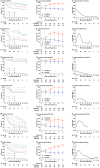
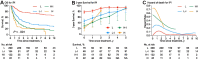
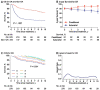
Typically, peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCLs) prognosis is estimated using overall survival before treatment. However, these estimates cannot show how prognosis evolves with the changing hazard rate over time. Patients (n = 650) with newly diagnosed PTCLs were enrolled retrospectively. After a median follow-up of 5.4 years, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (PTCL, NOS) and NK/T cell lymphoma had initially lower 3-year conditional overall survival (COS3; i.e., the 3-year conditional overall survival was defined as the probability of surviving an additional 3 years) and higher hazards of death (26-44.3%). However, after 2 years, the COS3 increased and the death risk decreased over time, whereas anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma constantly had a lower risk over time (0-19.5%). For patients with complete remission after initial treatment, prognosis varied by histological subtypes, with PTCL, NOS having a negative impact. Our data suggested that the risk stratification using the International Prognostic Index might not accurately predict the COS3 for survivors of PTCLs. The COS3 provided time-dependent prognostic information for PTCLs, representing a possible surrogate prognosis indicator for long-term survivors after systemic chemotherapy.
Keywords: T-cell; lymphoma; peripheral; prognosis; survival analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Liu W, Liu J, Song Y, Wang X, Zhou M, Wang L, Ma J, Zhu J, and Union for China Leukemia Investigators of the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology, Union for China Lymphoma Investigators of the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Mortality of lymphoma and myeloma in China, 2004-2017: an observational study. J Hematol Oncol. 2019; 12:22. 10.1186/s13045-019-0706-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

