The effects of carbon emissions, rainfall, temperature, inflation, population, and unemployment on economic growth in Saudi Arabia: An ARDL investigation
- PMID: 33819275
- PMCID: PMC8021147
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248743
The effects of carbon emissions, rainfall, temperature, inflation, population, and unemployment on economic growth in Saudi Arabia: An ARDL investigation
Abstract
Objective: While macroeconomic and environmental events affect the overall economic performance of nations, there has not been much research on the effects of important macroeconomic and environmental variables and how these can influence progress. Saudi Arabia's economy relies heavily on its vast reserves of petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, gold, and copper, but its economic growth trajectory has been uneven since the 1990s. This study examines the effects of carbon emissions, rainfall, temperature, inflation, population, and unemployment on economic growth in Saudi Arabia.
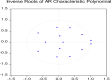
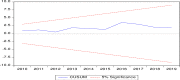
Methods: Annual time series dataset covering the period 1990-2019 has been extracted from the World Bank and General Authority of Meteorology and Environmental Protection, Saudi Arabia. The Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) approach to cointegration has served to investigate the long-run relationships among the variables. Several time-series diagnostic tests have been conducted on the long-term ARDL model to check its robustness.
Results: Saudi Arabia can still achieve higher economic growth without effectively addressing its unemployment problem as both the variables are found to be highly significantly but positively cointegrated in the long-run ARDL model. While the variable of carbon emissions demonstrated a negative effect on the nation's economic growth, the variables of rainfall and temperate were to some extent cointegrated into the nation's economic growth in negative and positive ways, respectively. Like most other nations the short-run effects of inflation and population on economic growth do vary, but their long-term effects on the same are found to be positive.
Conclusions: Saudi Arabia can achieve both higher economic growth and lower carbon emissions simultaneously even without effectively addressing the unemployment problem. The nation should utilize modern scientific technologies to annual rainfall losses and to reduce annual temperature in some parts of the country in order to achieve higher economic growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Energy, technology, and economic growth in Saudi Arabia: An ARDL and VECM analysis approach.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 8;10(4):e26033. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26033. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38384577 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon dioxide emissions, economic growth, energy use, and urbanization in Saudi Arabia: evidence from the ARDL approach and impulse saturation break tests.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 May;25(15):14882-14898. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1698-7. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29546516
-
Nexus between financial development and CO2 emissions in Saudi Arabia: analyzing the role of globalization.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Oct;25(28):28378-28390. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2876-3. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30083902
-
Water scarcity in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Apr;31(19):27554-27565. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-33024-3. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38587779 Review.
-
Economic Diversification Trends in the Gulf: the Case of Saudi Arabia.Circ Econ Sustain. 2022;2(1):221-230. doi: 10.1007/s43615-021-00106-0. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Circ Econ Sustain. 2022. PMID: 34888575 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Examining how unemployment, inflation and their related aspects affected economic growth in Palestine: The period from 1991 to 2020.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 20;9(11):e21081. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21081. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37920518 Free PMC article.
-
Natural disasters, deforestation, and emissions affect economic growth in Somalia.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 18;10(6):e28214. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28214. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38545204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kibria U, Arshadm M, Kamran M, Mehmood Y, Imdad S, Sajid M (2014) Exploring the impact of macro economic variables on GDP growth in Pakistan. Research Journal of Management Sciences 3(9): 1–6.
-
- Odusola A, Abidoye B (2015) Effects of temperature and rainfall shocks on economic growth in Africa. Available at SSRN 3101790.
-
- Colacito R, Hoffmann B, Phan T (2018) Temperatures and growth: A panel analysis of the United States. Journal of Money, Credit, and Banking 51(2–3): 313–368.
-
- Naser A-T (2016) Saudi Arabia’s Oil Dependence: Challenges Ahead. Italian Institute for International Political Studies (ISPI), Retrieved from https://www.ispionline.it/it/pubblicazione/saudi-arabias-oil-dependence-....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources