The impact of first and second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in society: comparative analysis to support control measures to cope with negative effects of future infectious diseases
- PMID: 33819476
- PMCID: PMC8017951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111099
The impact of first and second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in society: comparative analysis to support control measures to cope with negative effects of future infectious diseases
Abstract
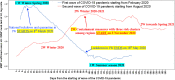
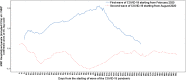
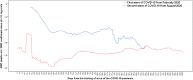
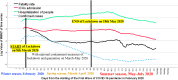
The goal of this study is a comparative analysis of the first and second wave of the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) to assess the impact on health of people for designing effective policy responses to constrain negative effects of future pandemic waves of COVID-19 and similar infectious diseases in society. The research here focuses on a case study of Italy, one of the first countries to experience a rapid increase in numbers of COVID-19 related infected individuals and deaths. Statistical analyses, based on daily data from February 2020 to February 2021, suggest that the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic in Italy had a high negative impact on health of people over February-May 2020 period; after that, negative effects declined from June 2020 onwards. Second wave of COVID-19 pandemic from August 2020 to February 2021 had a growing incidence of confirmed cases also associated with variants of coronavirus, whereas admissions to Intensive Care Units and total deaths had lower levels compared to first wave of COVID-19. Lessons learned of this comparative analysis between first and second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Italy can be generalized in similar geo-economic areas to support effective policy responses of crisis management to constrain the negative impact on health of people of recurring waves of COVID-19 pandemic and similar infectious diseases in future.
Keywords: COVID-19; Containment measures; Country monitoring; Crisis management; Health systems; Healthcare sector; Pandemic response; Preventing transmission; Public health; Public health capacity; Public policy.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author,
Figures

References
-
- Ardito L., Coccia M., Messeni Petruzzelli A. Technological exaptation and crisis management: evidence from COVID-19 outbreaks. R. Manag. 2021 doi: 10.1111/radm.12455. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

