Immunogenicity and antigenicity based T-cell and B-cell epitopes identification from conserved regions of 10664 SARS-CoV-2 genomes
- PMID: 33819681
- PMCID: PMC8017916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104823
Immunogenicity and antigenicity based T-cell and B-cell epitopes identification from conserved regions of 10664 SARS-CoV-2 genomes
Abstract
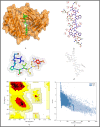
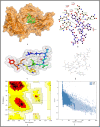
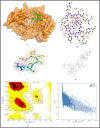
The surge of SARS-CoV-2 has created a wave of pandemic around the globe due to its high transmission rate. To contain this virus, researchers are working around the clock for a solution in the form of vaccine. Due to the impact of this pandemic, the economy and healthcare have immensely suffered around the globe. Thus, an efficient vaccine design is the need of the hour. Moreover, to have a generalised vaccine for heterogeneous human population, the virus genomes from different countries should be considered. Thus, in this work, we have performed genome-wide analysis of 10,664 SARS-CoV-2 genomes of 73 countries around the globe in order to identify the potential conserved regions for the development of peptide based synthetic vaccine viz. epitopes with high immunogenic and antigenic scores. In this regard, multiple sequence alignment technique viz. Clustal Omega is used to align the 10,664 SARS-CoV-2 virus genomes. Thereafter, entropy is computed for each genomic coordinate of the aligned genomes. The entropy values are then used to find the conserved regions. These conserved regions are refined based on the criteria that their lengths should be greater than or equal to 60 nt and their corresponding protein sequences are without any stop codons. Furthermore, Nucleotide BLAST is used to verify the specificity of the conserved regions. As a result, we have obtained 17 conserved regions that belong to NSP3, NSP4, NSP6, NSP8, RdRp, Helicase, endoRNAse, 2'-O-RMT, Spike glycoprotein, ORF3a protein, Membrane glycoprotein and Nucleocapsid protein. Finally, these conserved regions are used to identify the T-cell and B-cell epitopes with their corresponding immunogenic and antigenic scores. Based on these scores, the most immunogenic and antigenic epitopes are then selected for each of these 17 conserved regions. Hence, we have obtained 30 MHC-I and 24 MHC-II restricted T-cell epitopes with 14 and 13 unique HLA alleles and 21 B-cell epitopes for the 17 conserved regions. Moreover, for validating the relevance of these epitopes, the binding conformation of the MHC-I and MHC-II restricted T-cell epitopes are shown with respect to HLA alleles. Also, the physico-chemical properties of the epitopes are reported along with Ramchandran plots and Z-Scores and the population coverage is shown as well. Overall, the analysis shows that the identified epitopes can be considered as potential candidates for vaccine design.
Keywords: B-cell epitopes; Conserved regions; Epitopes; SARS-CoV-2; Synthetic vaccine; T-cell epitopes.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of Indian SARS-CoV-2 genomes to identify T-cell and B-cell epitopes from conserved regions based on immunogenicity and antigenicity.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Feb;91:107276. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107276. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33385714 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics pipeline unveils genetic variability to synthetic vaccine design for Indian SARS-CoV-2 genomes.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Nov;112:109224. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109224. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36116149 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of epitope-based vaccine design against the novel SARS-CoV-2.Infect Dis Poverty. 2020 Jul 10;9(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00713-3. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020. PMID: 32741372 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Coronavirus Vaccine Design Using Reverse Vaccinology and Machine Learning.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 3;11:1581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01581. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32719684 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Candidate Epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 Proteins for South America: A Review of HLA Frequencies by Country.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 3;11:2008. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02008. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping Potential Vaccine Candidates Predicted by VaxiJen for Different Viral Pathogens between 2017-2021-A Scoping Review.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;10(11):1785. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111785. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366294 Free PMC article.
-
Limited Recognition of Highly Conserved Regions of SARS-CoV-2.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0278021. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02780-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196796 Free PMC article.
-
A novel vaccine based on SARS-CoV-2 CD4+ and CD8+ T cell conserved epitopes from variants Alpha to Omicron.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 6;12(1):16731. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21207-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36202985 Free PMC article.
-
Designing a multi-epitope universal vaccine for concurrent infections of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses using an immunoinformatics approach.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 May 10;25(1):688. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11066-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40348967 Free PMC article.
-
Predicted B Cell Epitopes Highlight the Potential for COVID-19 to Drive Self-Reactive Immunity.Front Bioinform. 2021 Aug 19;1:709533. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2021.709533. eCollection 2021. Front Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 36303764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bency J., Helen M. Novel epitope based peptides for vaccine against sars-cov-2 virus: immunoinformatics with docking approach. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2020;8:2385. doi: 10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20202875. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

