Metabolic Control of Memory T-Cell Generation and Stemness
- PMID: 33820774
- PMCID: PMC8168429
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a037770
Metabolic Control of Memory T-Cell Generation and Stemness
Abstract
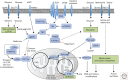
The formation of long-lived memory T cells is a critical feature of the adaptive immune response. T cells undergo metabolic reprogramming to establish a functional memory population. While initial studies characterized key metabolic pathways necessary for memory T-cell development, recent findings highlight that metabolic regulation of memory T-cell subsets is diverse. Here we describe the different requirements for metabolic programs and metabolism-related signaling pathways in memory T-cell development. We further discuss the contribution of cellular metabolism to memory T-cell functional reprogramming and stemness within acute and chronic inflammatory environments. Last, we highlight knowledge gaps and propose approaches to determine the roles of metabolites and metabolic enzymes in memory T-cell fate. Understanding how cellular metabolism regulates a functionally diverse memory population will undoubtedly provide new therapeutic insights to modulate protective T-cell immunity in human disease.
Copyright © 2021 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bachem A, Makhlouf C, Binger KJ, de Souza DP, Tull D, Hochheiser K, Whitney PG, Fernandez-Ruiz D, Dähling S, Kastenmuller W, et al. 2019. Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids promote the memory potential of antigen-activated CD8+ T cells. Immunity 51: 285–297. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
