An impact study of COVID-19 on six different industries: Automobile, energy and power, agriculture, education, travel and tourism and consumer electronics
- PMID: 33821074
- PMCID: PMC8014102
- DOI: 10.1111/exsy.12677
An impact study of COVID-19 on six different industries: Automobile, energy and power, agriculture, education, travel and tourism and consumer electronics
Abstract
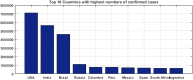
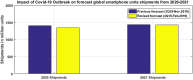
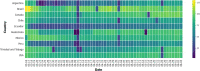
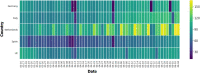
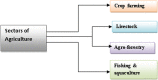
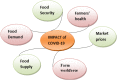
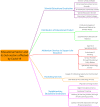
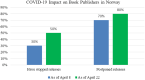
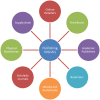
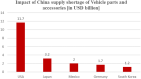
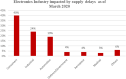
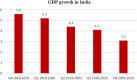
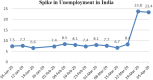
The recent outbreak of a novel coronavirus, named COVID-19 by the World Health Organization (WHO) has pushed the global economy and humanity into a disaster. In their attempt to control this pandemic, the governments of all the countries have imposed a nationwide lockdown. Although the lockdown may have assisted in limiting the spread of the disease, it has brutally affected the country, unsettling complete value-chains of most important industries. The impact of the COVID-19 is devastating on the economy. Therefore, this study has reported about the impact of COVID-19 epidemic on various industrial sectors. In this regard, the authors have chosen six different industrial sectors such as automobile, energy and power, agriculture, education, travel and tourism and consumer electronics, and so on. This study will be helpful for the policymakers and government authorities to take necessary measures, strategies and economic policies to overcome the challenges encountered in different sectors due to the present pandemic.
Keywords: COVID‐19; WHO; agriculture; automobile; consumer electronics energy and power; education; industry; pandemic; travel and tourism.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures






References
-
- WHO, World Health Organization . (2020). Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) in suspected human cases: interim guidance, 2 March 2020. No. WHO/COVID‐19/laboratory/2020.4. World Health Organization.
-
- Burch, T. R. , Emery, D. R. , & Fuerst, M. E. (2016). Who moves markets in a sudden marketwide crisis? Evidence from 9/11. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 51(2), 463–487.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
