Cardiac measurement of hyperpolarized 13 C metabolites using metabolite-selective multi-echo spiral imaging
- PMID: 33821504
- PMCID: PMC8212421
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28796
Cardiac measurement of hyperpolarized 13 C metabolites using metabolite-selective multi-echo spiral imaging
Abstract
Purpose: Noninvasive imaging with hyperpolarized (HP) pyruvate can capture in vivo cardiac metabolism. For proper quantification of the metabolites and optimization of imaging parameters, understanding MR characteristics such as s of the HP signals is critical. This study is to measure in vivo cardiac s of HP [1-13 C]pyruvate and the products in rodents and humans.
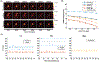
Methods: A dynamic 13 C multi-echo spiral imaging sequence that acquires [13 C]bicarbonate, [1-13 C]lactate, and [1-13 C]pyruvate images in an interleaved manner was implemented for a clinical 3 Tesla system. of each metabolite was calculated from the multi-echo images by fitting the signal decay of each region of interest mono-exponentially. The performance of measuring using the sequence was first validated using a 13 C phantom and then with rodents following a bolus injection of HP [1-13 C]pyruvate. In humans, of each metabolite was calculated for left ventricle, right ventricle, and myocardium.
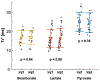
Results: Cardiac s of HP [1-13 C]pyruvate, [1-13 C]lactate, and [13 C]bicarbonate in rodents were measured as 24.9 ± 5.0, 16.4 ± 4.7, and 16.9 ± 3.4 ms, respectively. In humans, of [1-13 C]pyruvate was 108.7 ± 22.6 ms in left ventricle and 129.4 ± 8.9 ms in right ventricle. of [1-13 C]lactate was 40.9 ± 8.3, 44.2 ± 5.5, and 43.7 ± 9.0 ms in left ventricle, right ventricle, and myocardium, respectively. of [13 C]bicarbonate in myocardium was 64.4 ± 2.5 ms. The measurements were reproducible and consistent over time after the pyruvate injection.
Conclusion: The proposed metabolite-selective multi-echo spiral imaging sequence reliably measures in vivo cardiac s of HP [1-13 C]pyruvate and products.
Keywords: ; dynamic nuclear polarization; heart; hyperpolarized pyruvate; multi-echo spiral imaging.
© 2021 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures






References
-
- Golman K, Petersson JS, Magnusson P, et al. Cardiac metabolism measured noninvasively by hyperpolarized 13C MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2008;59:1005–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

