Low NLRP3 expression predicts a better prognosis of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 33821998
- PMCID: PMC8055799
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20210280
Low NLRP3 expression predicts a better prognosis of colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation is a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Whether NLRP3 is involved in the progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) remains elucidated and is the focus of the present study.
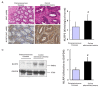
Methods: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was applied on tissue microarray (TMA) to determine the expression of NLRP3 in CRC patients. All 100 patients were divided into the low NLRP3 group and the high NLRP3 group according to their NLRP3 IHC scoring. Additionally, CRC xenografts were established by injecting HCT116 or RKO cells subcutaneously into nude mice. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were determined in HCT116 cells after treatment with NLRP3 inhibitor MCC950.
Results: NLRP3 expression was up-regulated in colon adenocarcinoma tissues compared with that in paracancerous tissues in CRC patients, HCT116 xenograft, and RKO xenograft. High NLRP3 level correlated with the advanced TNM classification of malignant tumors, the occurrence of distant metastasis, vascular invasion, and positive lymph nodes. Furthermore, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed that a high NLRP3 level was associated with a low 5-year survival rate and even a low 10-year survival rate. Moreover, the multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression model implied that NLRP3 expression level was an independent risk factor for CRC prognosis. Inhibition of NLRP3 by MCC950 suppressed cell proliferation, induced cell apoptosis, and decreased mRNA levels of interleukin 1β (IL1β) and interleukin 18 (IL18) in HCT116 cells.
Conclusions: High level of NLRP3 predicts poor survival in CRC patients. NLRP3 is a putative prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target in CRC treatments.
Keywords: Survival analysis; colon adenocarcinoma; inflammasome; interleukin 18; interleukin 1β.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

