Influence of saccharide modifications on heparin lyase III substrate specificities
- PMID: 33822051
- PMCID: PMC8966481
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwab023
Influence of saccharide modifications on heparin lyase III substrate specificities
Abstract
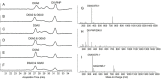
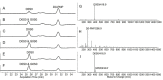
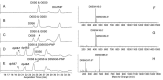
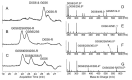
A library of 23 synthetic heparan sulfate (HS) oligosaccharides, varying in chain length, types, and positions of modifications, was used to analyze the substrate specificities of heparin lyase III enzymes from both Flavobacterium heparinum and Bacteroides eggerthii. The influence of specific modifications, including N-substitution, 2-O sulfation, 6-O sulfation, and 3-O sulfation on lyase III digestion was examined systematically. It was demonstrated that lyase III from both sources can completely digest oligosaccharides lacking O-sulfates. 2-O Sulfation completely blocked cleavage at the corresponding site; 6-O and 3-O sulfation on glucosamine residues inhibited enzyme activity. We also observed that there are differences in substrate specificities between the two lyase III enzymes for highly sulfated oligosaccharides. These findings will facilitate obtaining and analyzing the functional sulfated domains from large HS polymer, to better understand their structure/function relationships in biological processes.
Keywords: glycomics; glycosaminoglycans; heparan sulfate; heparin lyase; mass spectrometry.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The 3-O-sulfation of heparan sulfate modulates protein binding and lyase degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 19;118(3):e2012935118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012935118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33441484 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate specificity of the heparin lyases from Flavobacterium heparinum.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Nov 1;306(2):461-8. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1538. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993. PMID: 8215450
-
Oligosaccharide substrate preferences of human extracellular sulfatase Sulf2 using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based glycomics approaches.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 15;9(8):e105143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105143. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25127119 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-faceted substrate specificity of heparanase.Matrix Biol. 2013 Jun 24;32(5):223-7. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.02.006. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Matrix Biol. 2013. PMID: 23499529 Review.
-
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of heparan sulfate and heparin.Nat Prod Rep. 2014 Dec;31(12):1676-85. doi: 10.1039/c4np00076e. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Nat Prod Rep. 2014. PMID: 25197032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heparinase Digestion of 3-O-Sulfated Sequences: Selective Heparinase II Digestion for Separation and Identification of Binding Sequences Present in ATIII Affinity Fractions of Bovine Intestinal Heparins.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 31;9:841726. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.841726. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35433769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen YH, Narimatsu Y, Clausen TM, Gomes C, Karlsson R, Steentoft C, Spliid CB, Gustavsson T, Salanti A, Persson A, et al. 2018. The GAGOme: A cell-based library of displayed glycosaminoglycans. Nat Methods. 15:881–888. - PubMed
-
- Desai UR, Wang HM, Linhardt RJ. 1993a. Specificity studies on the heparin lyases from Flavobacterium heparinum. Biochemistry. 32:8140–8145. - PubMed
-
- Desai UR, Wang HM, Linhardt RJ. 1993b. Substrate specificity of the heparin lyases from Flavobacterium heparinum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 306:461–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

