The metabolism-modulating activity of IL-17 signaling in health and disease
- PMID: 33822846
- PMCID: PMC8025242
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20202191
The metabolism-modulating activity of IL-17 signaling in health and disease
Abstract
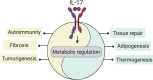
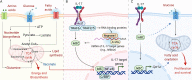
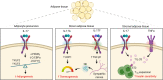
IL-17 was discovered nearly 30 yr ago, but it has only been recently appreciated that a key function of this cytokine is to orchestrate cellular and organismal metabolism. Indeed, metabolic regulation is integrated into both the physiological and the pathogenic aspects of IL-17 responses. Thus, understanding the interplay between IL-17 and downstream metabolic processes could ultimately inform therapeutic opportunities for diseases involving IL-17, including some not traditionally linked to this cytokine pathway. Here, we discuss the emerging pathophysiological roles of IL-17 related to cellular and organismal metabolism, including metabolic regulation of IL-17 signal transduction.
© 2021 Bechara et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pyruvate kinase: Function, regulation and role in cancer.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Jul;43:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.08.004. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26277545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Requirement for both JAK-mediated PI3K signaling and ACT1/TRAF6/TAK1-dependent NF-kappaB activation by IL-17A in enhancing cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells.J Immunol. 2007 Nov 15;179(10):6504-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.6504. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17982039
-
The role of mammalian sirtuins in cancer metabolism.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Jul;43:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.07.008. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26238985 Review.
-
The emerging roles of microRNAs in cancer metabolism.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt A):301–8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.011. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25451319 Review.
-
Adaptive regulation of glucose transport, glycolysis and respiration for cell proliferation.Biomol Concepts. 2015 Dec;6(5-6):423-30. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2015-0018. Biomol Concepts. 2015. PMID: 26418646 Review.
Cited by
-
Interpreting the Function of the IL-23/IL-17 Axis through Bioinformatics.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025;25(6):429-441. doi: 10.2174/0118715303316226240823045641. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39318016 Review.
-
Electroacupuncture Reduced Fibromyalgia-Pain-like Behavior through Inactivating Transient Receptor Potential V1 and Interleukin-17 in Intermittent Cold Stress Mice Model.Brain Sci. 2024 Aug 28;14(9):869. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14090869. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39335365 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of the synovial microenvironment and synovial mesenchymal stem cells with hip osteoarthritis of different bone morphologies.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Jan 10;26(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03252-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38200556 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the type 3 cytokines IL-17 and IL-22 in modulating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 2;15:1437046. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437046. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39156888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell metabolism-based therapy for liver fibrosis, repair, and hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2025 Jan 1;81(1):269-287. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000479. Epub 2023 May 23. Hepatology. 2025. PMID: 37212145 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amatya, N., Childs E.E., Cruz J.A., Aggor F.E.Y., Garg A.V., Berman A.J., Gudjonsson J.E., Atasoy U., and Gaffen S.L.. 2018. IL-17 integrates multiple self-reinforcing, feed-forward mechanisms through the RNA binding protein Arid5a. Sci. Signal. 11:eaat4617. 10.1126/scisignal.aat4617 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

