Cell-Free Biosynthesis to Evaluate Lasso Peptide Formation and Enzyme-Substrate Tolerance
- PMID: 33823110
- PMCID: PMC8062304
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c01452
Cell-Free Biosynthesis to Evaluate Lasso Peptide Formation and Enzyme-Substrate Tolerance
Abstract
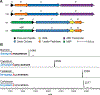
Lasso peptides are ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP) natural products that display a unique lariat-like, threaded conformation. Owing to a locked three-dimensional structure, lasso peptides can be unusually stable toward heat and proteolytic degradation. Some lasso peptides have been shown to bind human cell-surface receptors and exhibit anticancer properties, while others display antibacterial or antiviral activities. All known lasso peptides are produced by bacteria and genome-mining studies indicate that lasso peptides are a relatively prevalent class of RiPPs; however, the discovery, isolation, and characterization of lasso peptides are constrained by the lack of an efficient production system. In this study, we employ a cell-free biosynthesis (CFB) strategy to address longstanding challenges associated with lasso peptide production. We report the successful use of CFB for the formation of an array of sequence-diverse lasso peptides that include known examples as well as a new predicted lasso peptide from Thermobifida halotolerans. We further demonstrate the utility of CFB to rapidly generate and characterize multisite precursor peptide variants to evaluate the substrate tolerance of the biosynthetic pathway. By evaluating more than 1000 randomly chosen variants, we show that the lasso-forming cyclase from the fusilassin pathway is capable of producing millions of sequence-diverse lasso peptides via CFB. These data lay a firm foundation for the creation of large lasso peptide libraries using CFB to identify new variants with unique properties.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
M.J.B and D.A.M are co-founders of Lassogen, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Montalbán-López M; Scott TA; Ramesh S; Rahman IR; van Heel AJ; Viel JH; Bandarian V; Dittmann E; Genilloud O; Goto Y; Grande Burgos MJ; Hill C; Kim S; Koehnke J; Latham JA; Link AJ; Martínez B; Nair SK; Nicolet Y; Rebuffat S; Sahl H-G; Sareen D; Schmidt EW; Schmitt L; Severinov K; Süssmuth RD; Truman AW; Wang H; Weng J-K; van Wezel GP; Zhang Q; Zhong J; Piel J; Mitchell DA; Kuipers OP; van der Donk WA New Developments in RiPP Discovery, Enzymology and Engineering. Nat. Prod. Rep 2020, 38 (1), 130–239 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hegemann JD; Zimmermann M; Xie X; Marahiel MA Lasso Peptides: An Intriguing Class of Bacterial Natural Products. Acc. Chem. Res 2015, 48 (7), 1909–1919. - PubMed
-
- Arnison PG; Bibb MJ; Bierbaum G; Bowers AA; Bugni TS; Bulaj G; Camarero JA; Campopiano DJ; Challis GL; Clardy J; Cotter PD; Craik DJ; Dawson M; Dittmann E; Donadio S; Dorrestein PC; Entian K-D; Fischbach MA; Garavelli JS; Göransson U; Gruber CW; Haft DH; Hemscheidt TK; Hertweck C; Hill C; Horswill AR; Jaspars M; Kelly WL; Klinman JP; Kuipers OP; Link AJ; Liu W; Marahiel MA; Mitchell DA; Moll GN; Moore BS; Müller R; Nair SK; Nes IF; Norris GE; Olivera BM; Onaka H; Patchett ML; Piel J; Reaney MJT; Rebuffat S; Ross RP; Sahl H-G; Schmidt EW; Selsted ME; Severinov K; Shen B; Sivonen K; Smith L; Stein T; Süssmuth RD; Tagg JR; Tang G-L; Truman AW; Vederas JC; Walsh CT; Walton JD; Wenzel SC; Willey JM; van der Donk WA Ribosomally Synthesized and Post-Translationally Modified Peptide Natural Products: Overview and Recommendations for a Universal Nomenclature. Nat Prod Rep 2013, 30 (1), 108–160. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yan K-P; Li Y; Zirah S; Goulard C; Knappe TA; Marahiel MA; Rebuffat S Dissecting the Maturation Steps of the Lasso Peptide Microcin J25 in Vitro. Chembiochem 2012, 13 (7), 1046–1052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

