A central mechanism of analgesia in mice and humans lacking the sodium channel NaV1.7
- PMID: 33823138
- PMCID: PMC8110947
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.03.012
A central mechanism of analgesia in mice and humans lacking the sodium channel NaV1.7
Abstract
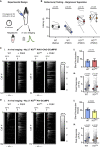
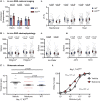
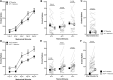
Deletion of SCN9A encoding the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.7 in humans leads to profound pain insensitivity and anosmia. Conditional deletion of NaV1.7 in sensory neurons of mice also abolishes pain, suggesting that the locus of analgesia is the nociceptor. Here we demonstrate, using in vivo calcium imaging and extracellular recording, that NaV1.7 knockout mice have essentially normal nociceptor activity. However, synaptic transmission from nociceptor central terminals in the spinal cord is greatly reduced by an opioid-dependent mechanism. Analgesia is also reversed substantially by central but not peripheral application of opioid antagonists. In contrast, the lack of neurotransmitter release from olfactory sensory neurons is opioid independent. Male and female humans with NaV1.7-null mutations show naloxone-reversible analgesia. Thus, inhibition of neurotransmitter release is the principal mechanism of anosmia and analgesia in mouse and human Nav1.7-null mutants.
Keywords: Na(V)1.7; analgesia; endogenous opioids; human genetics; neurotransmitter release; pain; sodium channels.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Locus revealed: Painlessness via loss of NaV1.7 at central terminals of sensory neurons.Neuron. 2021 May 5;109(9):1413-1416. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.04.011. Neuron. 2021. PMID: 33957067
References
-
- Alexandrou A.J., Brown A.R., Chapman M.L., Estacion M., Turner J., Mis M.A., Wilbrey A., Payne E.C., Gutteridge A., Cox P.J. Subtype-selective small molecule inhibitors reveal a fundamental role for Nav1.7 in nociceptor electrogenesis, axonal conduction and presynaptic release. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0152405. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

