Targeting autophagy in ischemic stroke: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics
- PMID: 33823204
- PMCID: PMC8263472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107848
Targeting autophagy in ischemic stroke: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics
Abstract
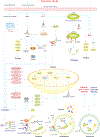
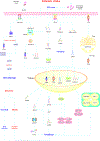
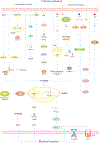
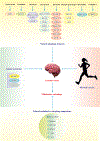
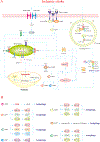
Stroke constitutes the second leading cause of death and a major cause of disability worldwide. Stroke is normally classified as either ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke (HS) although 87% of cases belong to ischemic nature. Approximately 700,000 individuals suffer an ischemic stroke (IS) in the US each year. Recent evidence has denoted a rather pivotal role for defective macroautophagy/autophagy in the pathogenesis of IS. Cellular response to stroke includes autophagy as an adaptive mechanism that alleviates cellular stresses by removing long-lived or damaged organelles, protein aggregates, and surplus cellular components via the autophagosome-lysosomal degradation process. In this context, autophagy functions as an essential cellular process to maintain cellular homeostasis and organismal survival. However, unchecked or excessive induction of autophagy has been perceived to be detrimental and its contribution to neuronal cell death remains largely unknown. In this review, we will summarize the role of autophagy in IS, and discuss potential strategies, particularly, employment of natural compounds for IS treatment through manipulation of autophagy.
Keywords: Adaptive autophagy; Cell death; Cerebral I/R injury; Ischemic stroke; Maladaptive autophagy.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ajoolabady A, Aghanejad A, Bi Y, Zhang Y, Aslkhodapasand HH, Abhari A, & Ren J (2020). Enzyme-based autophagy in anti-neoplastic management: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Reviews on Cancer, 188366. - PubMed
-
- Ajoolabady A, Aslkhodapasandhokmabad H, Aghanejad A, Zhang Y, & Ren J (2020). Mitophagy Receptors and Mediators: Therapeutic Targets in the Management of Cardiovascular Ageing. Ageing Research Reviews, 101129. - PubMed
-
- Ajoolabady A, Wang S, Kroemer G, Klionsky DJ, Uversky VN, Sowers JR, Aslkhodapasandhokmabad H, Bi Y, Ge J, & Ren J (2021). ER stress in Cardiometabolic Diseases: from Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Endocrine Reviews. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

