Cullin-RING Ubiquitin Ligase Regulatory Circuits: A Quarter Century Beyond the F-Box Hypothesis
- PMID: 33823649
- PMCID: PMC8217159
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-090120-013613
Cullin-RING Ubiquitin Ligase Regulatory Circuits: A Quarter Century Beyond the F-Box Hypothesis
Abstract
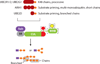
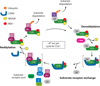
Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRLs) are dynamic modular platforms that regulate myriad biological processes through target-specific ubiquitylation. Our knowledge of this system emerged from the F-box hypothesis, posited a quarter century ago: Numerous interchangeable F-box proteins confer specific substrate recognition for a core CUL1-based RING E3 ubiquitin ligase. This paradigm has been expanded through the evolution of a superfamily of analogous modular CRLs, with five major families and over 200 different substrate-binding receptors in humans. Regulation is achieved by numerous factors organized in circuits that dynamically control CRL activation and substrate ubiquitylation. CRLs also serve as a vast landscape for developing small molecules that reshape interactions and promote targeted ubiquitylation-dependent turnover of proteins of interest. Here, we review molecular principles underlying CRL function, the role of allosteric and conformational mechanisms in controlling substrate timing and ubiquitylation, and how the dynamics of substrate receptor interchange drives the turnover of selected target proteins to promote cellular decision-making.
Keywords: E3 ligase; F-box protein; NEDD8; cullin; cullin-RING ligase; ubiquitin.
Figures



References
-
- Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, et al. 1996. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell 86:263–74 - PubMed
-
- Schwob E, Bohm T, Mendenhall MD, Nasmyth K. 1994. The B-type cyclin kinase inhibitor p40SIC1 controls the G1 to S transition in S. cerevisiae. Cell 79:233–44 - PubMed
-
- Willems AR, Lanker S, Patton EE, Craig KL, Nason TF, et al. 1996. Cdc53 targets phosphorylated G1 cyclins for degradation by the ubiquitin proteolytic pathway. Cell 86:453–63 - PubMed
-
- Feldman RM, Correll CC, Kaplan KB, Deshaies RJ. 1997. A complex of Cdc4p, Skp1p, and Cdc53p/cullin catalyzes ubiquitylation of the phosphorylated CDK inhibitor Sic1p. Cell 91:221–30 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

