Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block versus thoracic paravertebral block on postoperative analgesia after laparoscopic nephroureterectomy: study protocol of a randomized, double-blinded, non-inferiority design trial
- PMID: 33823924
- PMCID: PMC8022408
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-021-05173-0
Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block versus thoracic paravertebral block on postoperative analgesia after laparoscopic nephroureterectomy: study protocol of a randomized, double-blinded, non-inferiority design trial
Abstract
Introduction: Erector spinae plane block (ESPB) is a novel inter-fascial plane block, which is applied more and more in postoperative pain control, especially in chest surgery. Regional block is advocated in order to decrease opioid consumption and improve analgesia in urological surgery. Therefore, we aimed to explore whether ESPB would have similar analgesia compared with thoracic paravertebral block (TPVB) in laparoscopic nephroureterectomy.
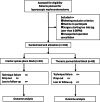
Methods and analysis: This prospective, randomized, double-blinded, non-inferiority trial will enroll 166 patients undergoing laparoscopic nephroureterectomy. Participants will be randomly assigned 1:1 into receiving ESPB or TPVB before surgery. Both ultrasound-guided ESPB and TPVB will be performed with an injection of 0.375% ropivacaine 0.4 ml/kg before anesthesia induction. Standardized patients controlled intravenous analgesia (PCIA) will be applied for each patient. The primary endpoint is the joint of cumulative 24 h opioid (sufentanil) consumption and average pain score via numeric rating scale (NRS) at 24 h after surgery. Secondary endpoints include rescued analgesic demand, cumulative opioid consumption, and pain NRS scores at different preset timepoints within 48 h after surgery. Other predefined outcomes include clinical features of blockage, quality of recovery, subjective sleep quality, time to ambulation and diet, and adverse events, as well as length of stay in hospital and anesthesia cost.
Discussion: Previous studies investigating the analgesic efficacy of ESPB only concentrated on a single endpoint for postoperative pain evaluation, while studies focusing on the direct comparison between ESPB and TPVB in urological surgery are still lacking. Our study is the first trial in non-inferiority design of comparing ESPB and TPVB in patient undergoing laparoscopic nephroureterectomy, and the primary outcome is the joint endpoint of opioid consumption and pain NRS score.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry ChiCTR 2000031916 . Registered on 14 April 2020.
Keywords: Erector spinae plane block; Laparoscopic urological surgery; Pain control; Regional anesthesia and analgesia; Thoracic paravertebral block.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block on analgesia and quality of recovery after minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass surgery: protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Jan 19;25(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-07925-0. Trials. 2024. PMID: 38243276 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block for perioperative analgesia in patients undergoing laparoscopic nephrectomies surgery: a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07866-0. Trials. 2024. PMID: 38167138 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of postoperative analgesic effects of erector spinae plane block and quadratus lumborum block in laparoscopic liver resection: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2023 May 16;24(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07341-w. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37194102 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic efficacy and safety of erector spinae plane block in pediatric patients undergoing elective surgery: A systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Clin Anesth. 2024 Nov;98:111575. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2024.111575. Epub 2024 Aug 10. J Clin Anesth. 2024. PMID: 39128258
-
Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block for postoperative short-term outcomes in lumbar spine surgery: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Feb 17;102(7):e32981. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032981. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36800574 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Analgesia Effect after Ultrasound-Guided Laparoscopic Renal Surgery.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Dec 24;2021:6194806. doi: 10.1155/2021/6194806. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Dec 8;2022:9864768. doi: 10.1155/2022/9864768. PMID: 34976111 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of bilateral ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block on postoperative pain control in idiopathic scoliosis patients undergoing posterior spine fusion surgery: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Jul 22;25(1):498. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08331-2. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39039587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Compérat E, Zigeuner R, Sylvester RJ, Burger M, Cowan NC, Gontero P, van Rhijn BWG, Mostafid AH, Palou J, Shariat SF. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: 2017 Update. Eur Urol. 2018;73(1):111–122. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.07.036. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous