E-health StandingTall balance exercise for fall prevention in older people: results of a two year randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 33824131
- PMCID: PMC8022322
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.n740
E-health StandingTall balance exercise for fall prevention in older people: results of a two year randomised controlled trial
Erratum in
-
E-health StandingTall balance exercise for fall prevention in older people: results of a two year randomised controlled trial.BMJ. 2021 Aug 17;374:n1908. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n1908. BMJ. 2021. PMID: 34404632 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To test whether StandingTall, a home based, e-health balance exercise programme delivered through an app, could provide an effective, self-managed fall prevention programme for community dwelling older people.
Design: Assessor blinded, randomised controlled trial.
Setting: Older people living independently in the community in Sydney, Australia.
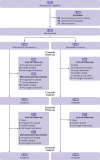
Participants: 503 people aged 70 years and older who were independent in activities of daily living, without cognitive impairment, progressive neurological disease, or any other unstable or acute medical condition precluding exercise.
Interventions: Participants were block randomised to an intervention group (two hours of StandingTall per week and health education; n=254) or a control group (health education; n=249) for two years.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcomes were the rate of falls (number of falls per person year) and the proportion of people who had a fall over 12 months. Secondary outcomes were the number of people who had a fall and the number who had an injurious fall (resulting in any injury or requiring medical care), adherence, mood, health related quality of life, and activity levels over 24 months; and balance and mobility outcomes over 12 months.
Results: The fall rates were not statistically different in the two groups after the first 12 months (0.60 falls per year (standard deviation 1.05) in the intervention group; 0.76 (1.25) in the control group; incidence rate ratio 0.84, 95% confidence interval 0.62 to 1.13, P=0.071). Additionally, the proportion of people who fell was not statistically different at 12 months (34.6% in intervention group, 40.2% in control group; relative risk 0.90, 95% confidence interval 0.67 to 1.20, P=0.461). However, the intervention group had a 16% lower rate of falls over 24 months compared with the control group (incidence rate ratio 0.84, 95% confidence interval 0.72 to 0.98, P=0.027). Both groups had a similar proportion of people who fell over 24 months (relative risk 0.87, 95% confidence interval 0.68 to 1.10, P=0.239), but the proportion of people who had an injurious fall over 24 months was 20% lower in the intervention group compared with the control group (relative risk 0.80, 95% confidence interval 0.66 to 0.98, P=0.031). In the intervention group, 68.1% and 52.0% of participants exercised for a median of 114.0 min/week (interquartile range 53.5) after 12 months and 120.4 min/week (38.6) after 24 months, respectively. Groups remained similar in mood and activity levels. The intervention group had a 0.03 (95% confidence interval 0.01 to 0.06) improvement on the EQ-5D-5L (EuroQol five dimension five level) utility score at six months, and an improvement in standing balance of 11 s (95% confidence interval 2 to 19 s) at six months and 10 s (1 to 19 s) at 12 months. No serious training related adverse events occurred.
Conclusions: The StandingTall balance exercise programme did not significantly affect the primary outcomes of this study. However, the programme significantly reduced the rate of falls and the number of injurious falls over two years, with similar but not statistically significant effects at 12 months. E-health exercise programmes could provide promising scalable fall prevention strategies.
Trial registration: ACTRN12615000138583.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf and declare: support from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, Gandel Philaptropy, NeuRA Foundation, National Heart Foundation, and Human Frontier Science Program for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Comment in
-
Critically appraised paper: Fall prevention program delivered electronically to community-dwelling older people can reduce fall rate over 24 months [commentary].J Physiother. 2022 Oct;68(4):279. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2022.09.002. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Physiother. 2022. PMID: 36244960 No abstract available.
-
Critically appraised paper: Fall prevention program delivered electronically to community-dwelling older people can reduce fall rate over 24 months.J Physiother. 2022 Oct;68(4):279. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2022.09.003. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Physiother. 2022. PMID: 36244963 No abstract available.
References
-
- Valenzuela T, Okubo Y, Woodbury A, Lord SR, Delbaere K. Adherence to technology-based exercise programs in older adults: a systematic review. J Geriatr Phys Ther 2018;41:49-61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
