Clinical Acquired Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition through a Novel KRAS Switch-II Pocket Mutation and Polyclonal Alterations Converging on RAS-MAPK Reactivation
- PMID: 33824136
- PMCID: PMC8338755
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0365
Clinical Acquired Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition through a Novel KRAS Switch-II Pocket Mutation and Polyclonal Alterations Converging on RAS-MAPK Reactivation
Abstract
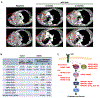
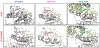
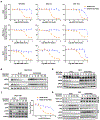
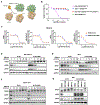
Mutant-selective KRASG12C inhibitors, such as MRTX849 (adagrasib) and AMG 510 (sotorasib), have demonstrated efficacy in KRAS G12C-mutant cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, mechanisms underlying clinical acquired resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors remain undetermined. To begin to define the mechanistic spectrum of acquired resistance, we describe a patient with KRAS G12C NSCLC who developed polyclonal acquired resistance to MRTX849 with the emergence of 10 heterogeneous resistance alterations in serial cell-free DNA spanning four genes (KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, MAP2K1), all of which converge to reactivate RAS-MAPK signaling. Notably, a novel KRAS Y96D mutation affecting the switch-II pocket, to which MRTX849 and other inactive-state inhibitors bind, was identified that interferes with key protein-drug interactions and confers resistance to these inhibitors in engineered and patient-derived KRAS G12C cancer models. Interestingly, a novel, functionally distinct tricomplex KRASG12C active-state inhibitor RM-018 retained the ability to bind and inhibit KRASG12C/Y96D and could overcome resistance. SIGNIFICANCE: In one of the first reports of clinical acquired resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors, our data suggest polyclonal RAS-MAPK reactivation as a central resistance mechanism. We also identify a novel KRAS switch-II pocket mutation that impairs binding and drives resistance to inactive-state inhibitors but is surmountable by a functionally distinct KRASG12C inhibitor.See related commentary by Pinnelli and Trusolino, p. 1874.This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 1861.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
The remaining authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
The gRASs Is Greener: Potential New Therapies in Lung Cancer with Acquired Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibitors.Cancer Discov. 2021 Aug;11(8):1874-1876. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0609. Cancer Discov. 2021. PMID: 34344756
References
-
- Hallin J, Engstrom LD, Hargis L, Calinisan A, Aranda R, Briere DM, et al. The KRAS(G12C) Inhibitor MRTX849 Provides Insight toward Therapeutic Susceptibility of KRAS-Mutant Cancers in Mouse Models and Patients. Cancer Discov 2020;10(1):54–71 doi 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1167. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

