Pembrolizumab-Associated CD8+ Vasculitic Mononeuritis Multiplex in a Patient With Mesothelioma
- PMID: 33824184
- PMCID: PMC8023979
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000993
Pembrolizumab-Associated CD8+ Vasculitic Mononeuritis Multiplex in a Patient With Mesothelioma
Figures
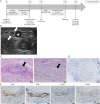
References
-
- Daxini A, Cronin K, Sreih AG. Vasculitis Associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors—A systematic review. Clinical Rheumatology Springer London; 2018:2579–2584. - PubMed
-
- Astaras C, de Micheli R, Moura B, Hundsberger T, Hottinger AF. Neurological adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: diagnosis and management. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2018:18:3. - PubMed
-
- Dubey D, David WS, Amato AA, et al. . Varied phenotypes and management of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated neuropathies. Neurology. 2019;93:e1093–e1103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
