Coordinated interactions between endothelial cells and macrophages in the islet microenvironment promote β cell regeneration
- PMID: 33824346
- PMCID: PMC8024255
- DOI: 10.1038/s41536-021-00129-z
Coordinated interactions between endothelial cells and macrophages in the islet microenvironment promote β cell regeneration
Abstract
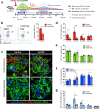
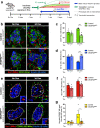
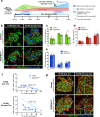
Endogenous β cell regeneration could alleviate diabetes, but proliferative stimuli within the islet microenvironment are incompletely understood. We previously found that β cell recovery following hypervascularization-induced β cell loss involves interactions with endothelial cells (ECs) and macrophages (MΦs). Here we show that proliferative ECs modulate MΦ infiltration and phenotype during β cell loss, and recruited MΦs are essential for β cell recovery. Furthermore, VEGFR2 inactivation in quiescent ECs accelerates islet vascular regression during β cell recovery and leads to increased β cell proliferation without changes in MΦ phenotype or number. Transcriptome analysis of β cells, ECs, and MΦs reveals that β cell proliferation coincides with elevated expression of extracellular matrix remodeling molecules and growth factors likely driving activation of proliferative signaling pathways in β cells. Collectively, these findings suggest a new β cell regeneration paradigm whereby coordinated interactions between intra-islet MΦs, ECs, and extracellular matrix mediate β cell self-renewal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The extra-islet pancreas supports autoimmunity in human type 1 diabetes.Elife. 2025 Apr 15;13:RP100535. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100535. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40232951 Free PMC article.
-
ABCG2-Expressing Clonal Repopulating Endothelial Cells Serve to Form and Maintain Blood Vessels.Circulation. 2024 Aug 6;150(6):451-465. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.061833. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Circulation. 2024. PMID: 38682338 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of LATS1/2 Drives Endothelial Senescence-Associated Stemness (SAS) and Atherothrombotic Lesion Formation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 21:2025.06.19.660635. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.19.660635. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40667385 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation and reduction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(12):CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub2. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25515689
-
Type 1 Diabetes: A Guide to Autoimmune Mechanisms for Clinicians.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Aug;27 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):40-56. doi: 10.1111/dom.16460. Epub 2025 May 15. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40375390 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stressed β-cells contribute to loss of peri-islet extracellular matrix in type 1 diabetes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 27:2025.06.25.661601. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.25.661601. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40667128 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Pericytes modulate islet immune cells and insulin secretion through Interleukin-33 production in mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 9;14:1142988. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1142988. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36967785 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between islets and regulatory immune cells in health and type 1 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2021 Nov;64(11):2378-2388. doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05565-6. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 34550422 Review.
-
Vascular Contribution to Lung Repair and Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2023 Aug;69(2):135-146. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2022-0431TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37126595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mosaic ablation of pancreatic β cells induces de-differentiation and repetitive proliferation of residual β cells in adult mice.iScience. 2024 Aug 3;27(9):110656. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110656. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39310764 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- DK62641/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK97829/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK94199/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK89572/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DK066636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069603/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK104211/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R24 DK106755/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK097829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63439/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- UC4 DK104211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK062641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK072473/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK66636/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- U01 DK089572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK68764/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK117147/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK106755/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK094199/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK058404/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA68485/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- DK69603/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK068764/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK117147/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK066636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK063439/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK20593/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

