Graphomotor memory in Exner's area enhances word learning in the blind
- PMID: 33824412
- PMCID: PMC8024258
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01971-z
Graphomotor memory in Exner's area enhances word learning in the blind
Abstract
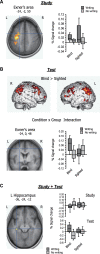
Handwriting is thought to impede vocabulary learning in sighted adults because the motor execution of writing interferes with efficient audiovisual processing during encoding. However, the motor memory of writing may facilitate adult word learning when visual sensory inputs are severely restricted. Using functional MRI, we show that late-blind participants, but not sighted participants, learned novel words by recruiting the left dorsal premotor cortex known as Exner's writing area and its functional coupling with the left hippocampus. During later recall, the phonological and semantic contents of these words are represented in the activation patterns of the left hippocampus as well as in those of left frontotemporal language areas. These findings suggest that motor codes of handwriting help blind participants maintain word-form representations during learning and retrieval. We propose that such reliance on the motor system reflects a broad architecture of the cerebral language network which encompasses the limb motor system as a hardwired component.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

