Non-inferior long-term outcomes of adults with Philadelphia chromosome-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 33824439
- PMCID: PMC8338554
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-021-01253-6
Non-inferior long-term outcomes of adults with Philadelphia chromosome-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
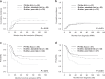
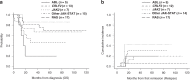
Philadelphia chromosome-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph-like ALL) is associated with inferior outcomes in the chemotherapy setting. We hypothesized that allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT)-based post-remission therapy would improve outcomes of this entity. We examined the frequency and long-term outcomes of adults with Ph-like ALL, particularly focusing on allo-HCT outcomes for Ph-like ALL versus non-Ph-like ALL. Ph-like ALL was determined by anchored multiplex PCR-based targeted next-generation sequencing. Of the 344 patients, 57 (16.6%) had Ph-like ALL, 197 (57.3%) had Ph-positive ALL, and 90 (26.1%) had B-other ALL. To further evaluate the prognosis of Ph-like ALL, outcome analyses were restricted to 147 patients, excluding Ph-positive ALL. The actual allo-HCT rates in complete remission were 87.7% for Ph-like ALL, 71.4% for B-other standard-risk ALL, and 70.4% for B-other poor-risk ALL. Patients with Ph-like ALL had a higher 5-year overall survival (60.6% vs 27.1%; P = 0.008) than B-other poor-risk ALL subgroup, while no difference was observed compared with B-other standard-risk ALL subgroup. Similar results were noted in a separate analysis for patients receiving allo-HCT in complete remission. In multivariate analyses, B-other poor-risk ALL was associated with poorer outcomes. Our data showed that allo-HCT-based post-remission therapy may have contributed to non-inferior outcomes of adult Ph-like ALL.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, Tallman MS, Buck G, Fielding AK, et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993) Blood. 2008;111:1827–33. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-116582. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Den Boer ML, van Slegtenhorst M, De Menezes RX, Cheok MH, Buijs-Gladdines JG, Peters ST, et al. A subtype of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with poor treatment outcome: a genome-wide classification study. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:125–34. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(08)70339-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

