Integration of 5G and Block-Chain Technologies in Smart Telemedicine Using IoT
- PMID: 33824715
- PMCID: PMC8007349
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8814364
Integration of 5G and Block-Chain Technologies in Smart Telemedicine Using IoT
Abstract
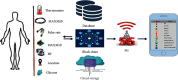
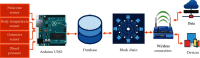
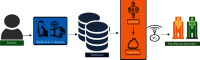
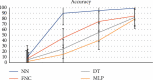
The Internet of Health Thing (IoHT) has various applications in healthcare. Modern IoHTintegrates health-related things like sensors and remotely observed medical devices for the assessment and managment of a patient's record to provide smarter and efficient health diagnostics to the patient. In this paper, we proposed an IoT with a cloud-based clinical decision support system for prediction and observation of disease with its severity level with the integration of 5G services and block-chain technologies. A block-chain is a system for storing and sharing information that is secure because of its transparency. Block-chain has many applications in healthcare and can improve mobile health applications, monitoring devices, sharing and storing of the electronic media records, clinical trial data, and insurance information storage. The proposed framework will collect the data of patients through medical devices that will be attached to the patient, and these data will be stored in a cloud server with relevant medical records. Deployment of Block-chain and 5G technology allows for sending patient data securely at a fast transmission rate with efficient response time. Furthermore, a Neural Network (NN) classifier is used for the prediction of diseases and their severity level. The proposed model is validated by employing different classifiers. The performance of different classifiers is measured by comparing the values to select the classifier that is the best for the dataset. The NN classifier attains an accuracy of 98.98. Furthermore, the NN is trained for the dataset so that it can predict the result of the dataset class that is not labeled. The trained Neural Network predicts and intelligently shows the results with more accuracy than other classifiers.
Copyright © 2021 Kashif Hameed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures










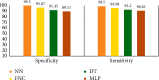
Similar articles
-
Smart Home-based IoT for Real-time and Secure Remote Health Monitoring of Triage and Priority System using Body Sensors: Multi-driven Systematic Review.J Med Syst. 2019 Jan 15;43(3):42. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1158-z. J Med Syst. 2019. PMID: 30648217
-
Potent Blockchain-Enabled Socket RPC Internet of Healthcare Things (IoHT) Framework for Medical Enterprises.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 8;22(12):4346. doi: 10.3390/s22124346. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746127 Free PMC article.
-
On the Design of Secured and Reliable Dynamic Access Control Scheme of Patient E-Healthcare Records in Cloud Environment.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Aug 18;2022:3804553. doi: 10.1155/2022/3804553. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Aug 9;2023:9878602. doi: 10.1155/2023/9878602. PMID: 36035822 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Enabling the Internet of Mobile Crowdsourcing Health Things: A Mobile Fog Computing, Blockchain and IoT Based Continuous Glucose Monitoring System for Diabetes Mellitus Research and Care.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jul 28;19(15):3319. doi: 10.3390/s19153319. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31357725 Free PMC article.
-
A Blockchain Framework for Patient-Centered Health Records and Exchange (HealthChain): Evaluation and Proof-of-Concept Study.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Aug 31;21(8):e13592. doi: 10.2196/13592. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31471959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improved Handover Authentication in Fifth-Generation Communication Networks Using Fuzzy Evolutionary Optimisation with Nanocore Elements in Mobile Healthcare Applications.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Jan 7;2022:2500377. doi: 10.1155/2022/2500377. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35035816 Free PMC article.
-
Internet of Medical Things Systems Review: Insights into Non-Functional Factors.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 29;25(9):2795. doi: 10.3390/s25092795. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40363233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Does Smart Healthcare Service Affect Resident Health in the Digital Age? Empirical Evidence From 105 Cities of China.Front Public Health. 2022 Jan 21;9:833687. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.833687. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35127633 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive IoT-Based e-Learning System: Enabling Context-Aware Remote Schooling during the Pandemic.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Aug 31;2021:7358874. doi: 10.1155/2021/7358874. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9802125. doi: 10.1155/2023/9802125. PMID: 34512940 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Shaikh A., Memon M., Memon N., Misbahuddin M. The role of service oriented architecture in telemedicine healthcare system. Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems; March 2009; Fukuoka, Japan. IEEE; pp. 208–214.
-
- Ling L., Dezhong Y., Jianqing L., Bin L., Ling W. A multimedia telemedicine system. Proceedings of the 2005 27th Annual Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology; January 2006; Shanghai, China. IEEE; pp. 3746–3748. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen D. C., Pathirana P. N., Ding M., Seneviratne A. Blockchain for 5G and beyond networks: a state of the art survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications. 2020;166 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102693.102693 - DOI
-
- Stradolini F., Tamburrano N., Modoux T., Tuoheti A., Demarchi D., Carrara S. IoT for telemedicine practices enabled by an Android™ application with cloud system integration. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS); May 2018; Florence, Italy. IEEE; pp. 1–5.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

