Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy
- PMID: 33824746
- PMCID: PMC8008077
- DOI: 10.4102/sajr.v25i1.2016
Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy
Abstract
Metronidazole is a widely used antibacterial and antiprotozoal agent for a number of conditions. Whilst its more common gastrointestinal side effects are well known, neurotoxicity remains under-recognised. Both central and peripheral neurological side effects have been described. This report describes a case of radiologically confirmed metronidazole-induced cerebellar ataxia in a cirrhotic patient with a review of the literature. Awareness of this side effect is essential for prompt recognition as early drug withdrawal leads to resolution in the majority of cases.
Keywords: corpus callosum lesions; dentate nucleus lesions; metronidazole; metronidazole adverse events; metronidazole-induced cerebellar ataxia; metronidazole-induced encephalopathy; metronidazole-induced neurotoxicity; splenium lesions.
© 2021. The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationships that may have inappropriately influenced them in writing this article.
Figures

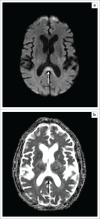
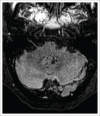

References
-
- Maddrey WC. Role of antibiotics in the management of hepatic encephalophathy. Rev Gastroenterol Disord [serial online]. [cited 2020 Apr 09]. 2005;5(SUPPL. 1):S3–S9. Available from: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-20544439543&partnerID... - PubMed
-
- McDonald LC, Gerding DN, Johnson S, et al. . Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults and children: 2017 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin Infect Dis. 2018;66(7):e1–e48. 10.1093/cid/cix1085 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
