Novel approaches to liver disease diagnosis and modeling
- PMID: 33824923
- PMCID: PMC7829068
- DOI: 10.21037/tgh-20-109
Novel approaches to liver disease diagnosis and modeling
Abstract
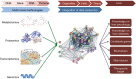
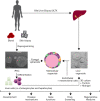
Lack of a prompt and accurate diagnosis remains on top of the list of challenges faced by patients with rare liver diseases. Although rare liver diseases affect a significant percentage of the population as a group, when taken singularly they represent unique diseases and the approaches used for diagnosis of common liver diseases are insufficient. However, the development of new methods for the acquisition of molecular and clinical data (i.e., genomic, proteomics, metabolomics) and computational tools for their analysis and integration, together with advances in modeling diseases using stem cell-based technology [i.e., induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and tissue organoids] represent a promising and powerful tool to improve the clinical management of these patients. This is the goal of precision medicine, a novel approach of modern medicine that aims at delivering a specific treatment based on disease-specific biological insights and individual profile. This review will discuss the application and advances of these technologies and how they represent a new opportunity in hepatology.
Keywords: Genomic; induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs); metabolomic; organoids; proteomic.
2021 Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tgh-20-109). The series “Recent Advances in Rare Liver Diseases” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus infection modeling using multi-cellular organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Aug 7;27(29):4784-4801. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i29.4784. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34447226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) and Cerebral Organoids for Drug Screening and Development in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Opportunities and Challenges.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Feb 19;13(2):280. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020280. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33669772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central nervous system organoids for modeling neurodegenerative diseases.IUBMB Life. 2022 Aug;74(8):812-825. doi: 10.1002/iub.2595. Epub 2022 Jan 31. IUBMB Life. 2022. PMID: 35102668 Review.
-
Next-Generation Liver Medicine Using Organoid Models.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Dec 20;7:345. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00345. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31921856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of induced pluripotent stem cell technology for the investigation of hematological disorders.Adv Biol Regul. 2019 Jan;71:19-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Adv Biol Regul. 2019. PMID: 30341008 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of Novel Biomarkers in Pediatric Autoimmune Hepatitis by Proteomic Profiling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 19;24(8):7479. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087479. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108648 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolite medicine offers a path beyond lists of metabolites.Commun Chem. 2021 Aug 5;4(1):115. doi: 10.1038/s42004-021-00551-w. Commun Chem. 2021. PMID: 36697841 Free PMC article.
-
Arouse potential stemness: Intrinsic and acquired stem cell therapeutic strategies for advanced liver diseases.Cell Insight. 2023 Aug 11;2(5):100115. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2023.100115. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cell Insight. 2023. PMID: 37719773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cells and regenerative medicine in sport science.Emerg Top Life Sci. 2021 Oct 29;5(4):563-573. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20210014. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34448473 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative Strategies in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Cirrhosis and Associated Syndromes.Life (Basel). 2025 May 13;15(5):779. doi: 10.3390/life15050779. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DNA Sequencing Costs: Data from the NHGRI Genome Sequencing Program (GSP). Available online: www.genome.gov/sequencingcostsdata
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
