Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia
- PMID: 33827113
- PMCID: PMC7611055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6
Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia
Abstract
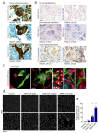
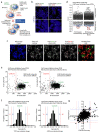
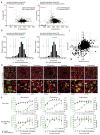
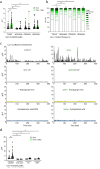
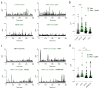
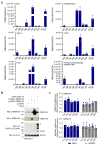
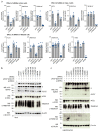
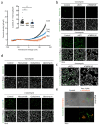
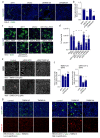
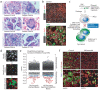
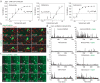
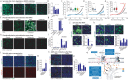
COVID-19 is a disease with unique characteristics that include lung thrombosis1, frequent diarrhoea2, abnormal activation of the inflammatory response3 and rapid deterioration of lung function consistent with alveolar oedema4. The pathological substrate for these findings remains unknown. Here we show that the lungs of patients with COVID-19 contain infected pneumocytes with abnormal morphology and frequent multinucleation. The generation of these syncytia results from activation of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein at the cell plasma membrane level. On the basis of these observations, we performed two high-content microscopy-based screenings with more than 3,000 approved drugs to search for inhibitors of spike-driven syncytia. We converged on the identification of 83 drugs that inhibited spike-mediated cell fusion, several of which belonged to defined pharmacological classes. We focused our attention on effective drugs that also protected against virus replication and associated cytopathicity. One of the most effective molecules was the antihelminthic drug niclosamide, which markedly blunted calcium oscillations and membrane conductance in spike-expressing cells by suppressing the activity of TMEM16F (also known as anoctamin 6), a calcium-activated ion channel and scramblase that is responsible for exposure of phosphatidylserine on the cell surface. These findings suggest a potential mechanism for COVID-19 disease pathogenesis and support the repurposing of niclosamide for therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
King’s College London has filed a patent application on the methods used to detect SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein-induced syncytia as described in this manuscript.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RG/20/3/34823/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 106223/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 106223/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CH/1999001/11735/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/N026063/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RE/18/2/34213/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R37 AI076119/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MR/W006251/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 215508/Z/19/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U54 AI150472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 215508/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 787971/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- RG/19/11/34633/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 AI076119/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

