Histotripsy: the first noninvasive, non-ionizing, non-thermal ablation technique based on ultrasound
- PMID: 33827375
- PMCID: PMC9404673
- DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2021.1905189
Histotripsy: the first noninvasive, non-ionizing, non-thermal ablation technique based on ultrasound
Abstract
Histotripsy is the first noninvasive, non-ionizing, and non-thermal ablation technology guided by real-time imaging. Using focused ultrasound delivered from outside the body, histotripsy mechanically destroys tissue through cavitation, rendering the target into acellular debris. The material in the histotripsy ablation zone is absorbed by the body within 1-2 months, leaving a minimal remnant scar. Histotripsy has also been shown to stimulate an immune response and induce abscopal effects in animal models, which may have positive implications for future cancer treatment. Histotripsy has been investigated for a wide range of applications in preclinical studies, including the treatment of cancer, neurological diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. Three human clinical trials have been undertaken using histotripsy for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, liver cancer, and calcified valve stenosis. This review provides a comprehensive overview of histotripsy covering the origin, mechanism, bioeffects, parameters, instruments, and the latest results on preclinical and human studies.
Keywords: High intensity ultrasound; imaging; immunotherapy; physics; ultrasound.
Figures
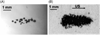



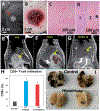
References
-
- Fakiris AJ, McGarry RC, Yiannoutsos CT, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung carcinoma: four-year results of a prospective phase II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75(3):677–682. - PubMed
-
- Lo SS, Fakiris AJ, Chang EL, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: a novel treatment modality. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7(1):44–54. - PubMed
-
- Kudo M. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: updated review in 2010. Oncology. 2010;78(1):113–124. - PubMed
-
- Martin RC, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM. Safety and efficacy of microwave ablation of hepatic tumors: a prospective review of a 5-year experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(1):171–178. - PubMed
-
- Lanza E, Palussiere J, Buy X, et al. Percutaneous image-guided cryoablation of breast cancer: a systematic review. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;26(11):1652–1657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
