Significance of coagulation and fibrinolysis markers for benign and malignant soft tissue tumors
- PMID: 33827473
- PMCID: PMC8028118
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08091-1
Significance of coagulation and fibrinolysis markers for benign and malignant soft tissue tumors
Abstract
Background: The intimate relationship between coagulation and fibrinolysis in malignant tumors is a well-known phenomena, with the malignant phenotype enhancing coagulation and fibrinolysis. We hypothesized that soft tissue sarcoma (STS) affects the expression of coagulation and fibrinolysis markers, which could be used to distinguish STS from benign soft tissue tumors. We analyzed the correlations between plasma levels of D-dimer (DD), plasmin-α2 plasmin inhibitor complex (PIC), soluble fibrin (SF), and thrombin-antithrombin III complex (TAT) in benign soft tissue tumors and STS to elucidate whether these markers can be used to predict STS.
Methods: Plasma DD, PIC, SF and TAT levels in primary soft tissue tumors (benign 67, STS 68) were measured before biopsy or treatment. The marker levels were analyzed and compared to various clinicopathological parameters.
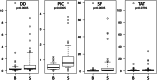
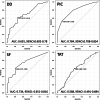
Results: In malignancy (STS), the average DD, PIC and SF levels were significantly higher than in benign tumors. Multivariate logistic analysis of continuous variables indicated that only PIC exhibited a significant difference (OR: 24.5, 95%CI: 3.55-170, p = 0.0012). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis produced area under the curve values for DD: 0.691, PIC: 0.784, SF: 0.734 and TAT: 0.588. Youden's index was used to establish thresholds of 0.37 (DD), 0.80 (PIC), 0.90 (SF) and 0.82 (TAT). Threshold values for PIC and SF indicated high specificity (0.881, 0.791) and high positive predictive value (0.818, 0.745), respectively. The highest accuracy value among the markers was observed for PIC (0.704). Significant differences in multivariate analysis of binary variables were demonstrated by categorizing low and high groups based on their threshold, PIC (≥0.80) (OR: 3.36, 95%CI: 1.19-9.43, p = 0.0212) and SF (≥0.90) (OR: 2.63, 95%CI: 1.04-6.66, p = 0.0404) .
Conclusions: Of the coagulation and fibrinolysis markers studied, increased PIC levels were related to STS and over 0.80 PIC was the most suitable for the prediction of STS, which, along with other diagnostic tools, represents a helpful subsidiary tool for the prediction of STS.
Keywords: And thrombin-antithrombin III complex; Coagulation; D-dimer; Fibrinolysis; Metastasis; Plasmin-α2 plasmin inhibitor complex; Prognosis; Soft tissue sarcoma; Soluble fibrin.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Soe G, Kohno I, Inuzuka K, Itoh Y, Matsuda M. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes a neo-antigen exposed in the E domain of fibrin monomer complexed with fibrinogen or its derivatives: its application to the measurement of soluble fibrin in plasma. 1996. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

