Striatum Hyperactivity Triggers Relapse to Morphine and Methamphetamine (Polydrug) Dependence in Mice
- PMID: 33828384
- PMCID: PMC8021060
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_379_19
Striatum Hyperactivity Triggers Relapse to Morphine and Methamphetamine (Polydrug) Dependence in Mice
Abstract
Introduction: κ-opioid receptor (KOPr) system has been linked to relapse to many substances, especially opioids. Positive responses were recently reported in morphine and methamphetamine (polydrug)-dependent mice treated with buprenorphine and naltrexone, a functional κ antagonist.
Objectives: This study aimed to determine the specific brain region that is responsive to KOPr treatment following polydrug dependence.
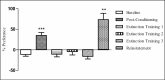
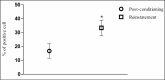
Materials and methods: The polydrug-dependent mice model was developed using conditioned place preference (CPP) method. Following successful withdrawal phase, the mice were treated with 0.3 mg/kg buprenorphine and 1.0 mg/kg naltrexone. Four brain regions (hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and striatum) were investigated using immunohistochemistry technique. This is to quantify the changes in KOPr expression in each major brain region that was primarily involved in addiction neurocircuits of many substances. Unpaired Student's t test was used to analyze all results, where P < 0.05 is considered significant.
Results: The results showed that treatment with buprenorphine and naltrexone successfully attenuated relapse in 60% of mice (n = 14). A significant upregulation of KOPr was detected in striatum at the end of post-withdrawal phase (P < 0.01, n = 12). This treatment successfully suppressed KOPr in striatum (P < 0.001, n = 12), which supports the positive results seen in the CPP setting. No significant changes were observed in other brain regions studied.
Conclusion: The hyperactivity of striatum suggests that the affected brain region following KOPr antagonist treatment is the region that primarily controls the drug rewarding activity, in which nucleus accumbens is located. This indicates that manipulation of KOPr system is one of the potential targets to treat morphine- or methamphetamine-dependence problem.
Keywords: Brain; drug addiction; kappa; methamphetamine; polydrug.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Koob GF. Neurocircuitry of alcohol addiction: synthesis from animal models. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;125:33–54. - PubMed
-
- Liu SH, Lin-Shiau SY, Chang AC, Lan KC. Clinical manifestations of combined methamphetamine with morphine and their effects on brain dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine release in mice. J Med Sci. 2015;35:194–200.
-
- Ridzwan IE, Suhaimi MS, Muhamad AH, Kasmuri AR, Mohamed Nazar NI, Hashim R, et al. Low-dose methamphetamine addiction induced opioid receptor sensitization in polydrug-dependent mice. Springer, Singapore: Regional Conference on Science, Technology and Social Sciences (RCSTSS 2016); 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
