Transient Astrocytic Gq Signaling Underlies Remote Memory Enhancement
- PMID: 33828463
- PMCID: PMC8019746
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2021.658343
Transient Astrocytic Gq Signaling Underlies Remote Memory Enhancement
Abstract
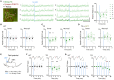
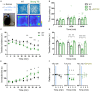
Astrocytes elicit transient Ca2+ elevations induced by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), yet their role in vivo remains unknown. To address this, transgenic mice with astrocytic expression of the optogenetic Gq-type GPCR, Optoα1AR, were established, in which transient Ca2+ elevations similar to those in wild type mice were induced by brief blue light illumination. Activation of cortical astrocytes resulted in an adenosine A1 receptor-dependent inhibition of neuronal activity. Moreover, sensory stimulation with astrocytic activation induced long-term depression of sensory evoked response. At the behavioral level, repeated astrocytic activation in the anterior cortex gradually affected novel open field exploratory behavior, and remote memory was enhanced in a novel object recognition task. These effects were blocked by A1 receptor antagonism. Together, we demonstrate that GPCR-triggered Ca2+ elevation in cortical astrocytes has causal impacts on neuronal activity and behavior.
Keywords: Ca2+ signaling; G protein-coupled receptor; OptoA1AR; astrocytes; memory; optogenetic activation.
Copyright © 2021 Iwai, Ozawa, Yahagi, Mishima, Akther, Vo, Lee, Tanaka, Itohara and Hirase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

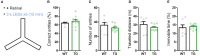

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

