The Cost Effectiveness of Immunoglobulin vs. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for CIDP
- PMID: 33828522
- PMCID: PMC8019941
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.645263
The Cost Effectiveness of Immunoglobulin vs. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for CIDP
Abstract
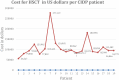
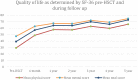
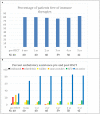
Background: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is effective as standard first line therapy for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP), but some patients remain dependent on its long-term use. Recently, we have reported that autologous non-myeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is an effective second line therapy for CIDP. Objectives: To compare the cost of chronic IVIG vs. autologous HSCT (a one-time therapy), we collected data on patients with CIDP undergoing HSCT between 2017 and 2019. This was compared with published literature on the costs and efficacy defined by the Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause And Treatment (INCAT) disability score, Medical Research Council (MRC) sum score, hand grip strength, and SF-36 quality of life (QOL) for CIDP. Methods: Between 2017 and 2019, nineteen patients with chronic CIDP (mean disease treatment duration prior to HSCT of 6 years) underwent autologous HSCT with mean cost of $108,577 per patient (range $56,327-277,119, standard deviation $53,092). After HSCT, 80% of patients remain IVIG and immune treatment free for up to 5 years. In comparison, published cost of IVIG treatment in the USA for an average CIDP patient exceeds $136,000 per year. Despite remaining treatment free, HSCT demonstrated greater improvement in efficacy compared to immunoglobulins. Recommendations: Given the long-term treatment-free remission and better outcome measurements, autologous HSCT is more cost effective than long-term IVIG treatment in patients with chronic CIDP. However, costs will depend on patient selection, the HSCT regimen, and regional variations. Further analysis of the health economics, i.e., cost/outcome ratio, of HSCT as therapy for chronically IVIG dependent CIDP is warranted.
Keywords: CIDP; cost; health economics; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; immunoglobulin.
Copyright © 2021 Burt, Tappenden, Balabanov, Han, Quigley, Snowden and Sharrack.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Van den Bergh PY, Hadden RD, Bouche P, Cornblath DR, Hahn A, Illa I, et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society—first revision. Eur J Neurol. (2010) 17:356–63. 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02930.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hughes RA, Donofrio P, Bril V, Dalakas MC, Deng C, Hanna K, et al. Intravenous immune globulin (10% caprylate-chromatography purified) for the treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (ICE study): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. (2008) 7:136–44. 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70329-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Schaik IN, Bril V, van Geloven N, Hartung HP, Lewis RA, Sobue G, et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin for maintenance treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (PATH): a randomized, double blinded, placebo controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. (2018) 17:35–46. 10.1186/s13063-016-1466-2 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

