Cloning and Characterization of TaSAP7-A, a Member of the Stress-Associated Protein Family in Common Wheat
- PMID: 33828570
- PMCID: PMC8020846
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.609351
Cloning and Characterization of TaSAP7-A, a Member of the Stress-Associated Protein Family in Common Wheat
Abstract
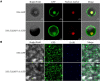
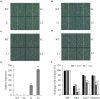
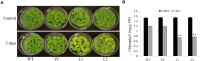
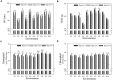
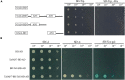
Stress association proteins (SAPs) are A20/AN1 zinc-finger domain proteins, which play important roles in plant adaptation to abiotic stress and plant development. The functions of SAPs in some plants were reported, but little is known about it in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). In this study, we characterized a novel 2AN1-type stress association protein gene TaSAP7-A, which was mapped to chromosome 5A in wheat. Subcellular localization indicated that TaSAP7-A was distributed in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Unlike previously known A20/AN1-type SAP genes, TaSAP7-A was negatively regulated to abiotic stress tolerance. Overexpressing TaSAP7-A Arabidopsis lines were hypersensitive to ABA, osmotic and salt stress at germination stage and post-germination stage. Overexpression of TaSAP7-A Arabidopsis plants accelerated the detached leaves' chlorophyll degradation. Association analysis of TaSAP7-A haplotypes and agronomic traits showed that Hap-5A-2 was significantly associated with higher chlorophyll content at jointing stage and grain-filling stage. These results jointly revealed that TaSAP7-A is related to the chlorophyll content in the leaves of Arabidopsis and wheat. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments demonstrated that TaSAP7-A interacted with TaS10B, which was the component of regulatory subunit in 26S proteasome. In general, TaSAP7-A was a regulator of chlorophyll content, and favorable haplotypes should be helpful for improving plant chlorophyll content and grain yield of wheat.
Keywords: TaS10B; TaSAP7-A; abiotic stress; chlorophyll content; wheat.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Wang, Li, Chang, Yuan and Jing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of TaWD40D, a wheat WD40 repeat-containing protein that is associated with plant tolerance to abiotic stresses.Plant Cell Rep. 2015 Mar;34(3):395-410. doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1717-1. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Plant Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25447637
-
Genomic Analysis of Stress Associated Proteins in Soybean and the Role of GmSAP16 in Abiotic Stress Responses in Arabidopsis and Soybean.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Nov 18;10:1453. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01453. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31803204 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of stress-associated proteins (SAPs) containing A20/AN1 zinc finger in cotton.Mol Genet Genomics. 2016 Dec;291(6):2199-2213. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1252-6. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Mol Genet Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27681253
-
TraeALDH7B1-5A, encoding aldehyde dehydrogenase 7 in wheat, confers improved drought tolerance in Arabidopsis.Planta. 2015 Jul;242(1):137-51. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2290-8. Epub 2015 Apr 18. Planta. 2015. PMID: 25893867
-
Arabidopsis stress associated protein 9 mediates biotic and abiotic stress responsive ABA signaling via the proteasome pathway.Plant Cell Environ. 2017 May;40(5):702-716. doi: 10.1111/pce.12892. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Plant Cell Environ. 2017. PMID: 28039858
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Profiling during Sequential Stages of Cryopreservation in Banana (Musa AAA cv Borjahaji) Shoot Meristem.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;12(5):1165. doi: 10.3390/plants12051165. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904022 Free PMC article.
-
Aeluropus littoralis stress-associated protein promotes water deficit resilience in engineered durum wheat.Heliyon. 2024 May 9;10(10):e30933. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30933. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38765027 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and evolution of the SAP gene family in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and expression analysis under salt and drought stress.PeerJ. 2024 Jul 30;12:e17808. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17808. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39099650 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Specific Alleles of Zinc-Finger Transcription Factors, HvSAP8 and HvSAP16, and Corresponding SNP Markers, Are Associated with Drought Tolerance in Barley Populations.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 10;22(22):12156. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212156. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhtar M., Jaiswal A., Taj G., Jaiswal J. P., Qureshi M. I., Singh N. K. (2012). DREB1/CBF transcription factors: their structure, function and role in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. J. Genet. 91 385–395. - PubMed
-
- Ben Saad R., Fabre D., Mieulet D., Meynard D., Dingkuhn M., Al-Doss A., et al. (2012). Expression of the Aeluropus littoralis AlSAP gene in rice confers broad tolerance to abiotic stresses through maintenance of photosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ. 35 626–643. 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02441.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ben Saad R., Zouari N., Ben Ramdhan W., Azaza J., Meynard D., Guiderdoni E., et al. (2010). Improved drought and salt stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco overexpressing a novel A20/AN1 zinc-finger “AlSAP” gene isolated from the halophyte grass Aeluropus littoralis. Plant Mol. Biol. 72 171–190. 10.1007/s11103-009-9560-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang J., Hao C., Chang X., Zhang X., Jing R. (2014). HapIII of TaSAP1-A1, a positively selected haplotype in wheat breeding. J. Integr. Agr. 13 1462–1468. 10.1016/s2095-3119(14)60808-x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

