Comparison of the precision of smooth pursuit in humans and head unrestrained monkeys
- PMID: 33828708
- PMCID: PMC7904314
- DOI: 10.16910/jemr.11.4.6
Comparison of the precision of smooth pursuit in humans and head unrestrained monkeys
Abstract
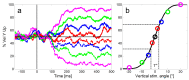
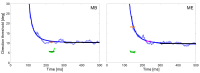
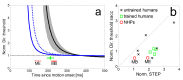
Direct comparison of results of humans and monkeys is often complicated by differences in experimental conditions. We replicated in head unrestrained macaques experiments of a recent study comparing human directional precision during smooth pursuit eye movements (SPEM) and saccades to moving targets (Braun & Gegenfurtner, 2016). Directional precision of human SPEM follows an exponential decay function reaching optimal values of 1.5°-3° within 300 ms after target motion onset, whereas precision of initial saccades to moving targets is slightly better. As in humans, we found general agreement in the devel-opment of directional precision of SPEM over time and in the differences between direc-tional precision of initial saccades and SPEM initiation. However, monkeys showed over-all lower precision in SPEM compared to humans. This was most likely due to differences in experimental conditions, such as in the stabilization of the head, which was by a chin and a head rest in human subjects and unrestrained in monkeys.
Keywords: Eye movement; eye tracking; head unrestrained; non-human primates; saccades; smooth pursuit.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the contents of the article are in agreement with the ethics described in http://biblio.unibe.ch/portale/elibrary/BOP/jemr/ethics.html and that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dynamics of oculomotor direction discrimination.J Vis. 2016 Oct 1;16(13):4. doi: 10.1167/16.13.4. J Vis. 2016. PMID: 27792805
-
[Study of non-visually induced smooth pursuit eye movements and their predictability using pseudorandom target motion].Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1997 Dec;100(12):1450-8. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.100.1450. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1997. PMID: 9465609 Japanese.
-
Non-visually induced smooth pursuit eye movements using sinusoidal target motion.Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1996;525:158-62. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8908293
-
Short-term adaptation of saccades does not affect smooth pursuit eye movement initiation.J Vis. 2017 Aug 1;17(9):19. doi: 10.1167/17.9.19. J Vis. 2017. PMID: 28837965
-
Abnormalities of smooth pursuit in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review.Clin Park Relat Disord. 2020 Dec 17;4:100085. doi: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2020.100085. eCollection 2021. Clin Park Relat Disord. 2020. PMID: 34316663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coding of interceptive saccades in parietal cortex of macaque monkeys.Brain Struct Funct. 2021 Nov;226(8):2707-2723. doi: 10.1007/s00429-021-02365-x. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Brain Struct Funct. 2021. PMID: 34468861 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
