Fixational Eye Movement Waveforms in Amblyopia: Characteristics of Fast and Slow Eye Movements
- PMID: 33828757
- PMCID: PMC7962684
- DOI: 10.16910/jemr.12.6.9
Fixational Eye Movement Waveforms in Amblyopia: Characteristics of Fast and Slow Eye Movements
Abstract
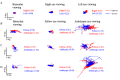
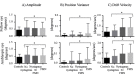
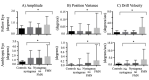
Fixational eye movements comprise of fast microsaccades alternating with slow intersaccadic drifts. These physiologic eye movements play an important role in visual perception. Amblyopic patients are known to have fixation instability, particularly of the amblyopic eye. We examined eye movement abnormalities that contribute to this instability. We found that fixation stability is affected by the presence of fusion maldevelopment nystagmus (FMN). However, some amblyopes can have nystagmus without nasally directed slow phases and reversal in direction of the quick phase on ocular occlusion, features seen in FMN. In patients without nystagmus, we found increased amplitude of fixational saccades and inter-saccadic drifts. We categorized amblyopia patients by type (anisometropic, strabismic, or mixed) and eye movement waveform (no nystagmus, nystagmus without FMN, and FMN). We found specific fast and slow eye movement abnormalities of the fellow and amblyopic eye during fellow, amblyopic and both eyes viewing conditions across eye movement waveforms and types of amblyopia. These eye movement abnormalities can serve as biomarkers that can predict the impact of amblyopia as measured by visual acuity and stereopsis. Evaluation of fixational eye movements in amblyopia could be important to diagnose these common eye diseases and predict treatment effectiveness.
Keywords: Eye movement; binocular viewing; fixational stability; microsaccades; saccades.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the contents of the article are in agreement with the ethics described in http://biblio.unibe.ch/portale/elibrary/BOP/jemr/ethics.html and that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
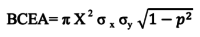



Similar articles
-
Part time patching treatment outcomes in children with amblyopia with and without fusion maldevelopment nystagmus: An eye movement study.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 13;15(8):e0237346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237346. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32790721 Free PMC article.
-
Fixation instability in amblyopia: Oculomotor disease biomarkers predictive of treatment effectiveness.Prog Brain Res. 2019;249:235-248. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2019.04.024. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Prog Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31325983 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Viewing Conditions on Fixation Eye Movements and Eye Alignment in Amblyopia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Feb 1;63(2):33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.2.33. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35212720 Free PMC article.
-
Amblyopia and fixation eye movements.J Neurol Sci. 2022 Oct 15;441:120373. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2022.120373. Epub 2022 Aug 3. J Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36007287 Review.
-
Attention deficits in Amblyopia.Curr Opin Psychol. 2019 Oct;29:199-204. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2019.03.011. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Curr Opin Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31030000 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating Eye Tracking During Dichoptic Video Viewing With Varied Fellow Eye Contrasts in Amblyopia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Dec 2;65(14):11. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.14.11. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39630462 Free PMC article.
-
Part time patching treatment outcomes in children with amblyopia with and without fusion maldevelopment nystagmus: An eye movement study.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 13;15(8):e0237346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237346. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32790721 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Assessment of Fixational Disparity Using a Binocular Eye-Tracking Technique in Children with Strabismus.J Eye Mov Res. 2025 Mar 10;18(2):6. doi: 10.3390/jemr18020006. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Eye Mov Res. 2025. PMID: 40290624 Free PMC article.
-
Dichoptic Visual Search at Varied Fellow Eye Contrasts and Visual Function Deficits in Amblyopia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jul 1;66(9):39. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.9.39. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40657969 Free PMC article.
-
Objective assessment of eye alignment and disparity-driven vergence in Parkinson's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Oct 31;15:1217765. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1217765. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38020777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birch EE, Castaneda YS, Cheng-Patel CS, Morale SE, Kelly KR, Beauchamp CL, et al. ( 2018). Self-perception of School-Aged Children With Amblyopia and Its Association With Reading Speed and Motor Skills. JAMA ophthalmology., 26( 3), 118–121. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2018.5527. PubMed PMID: 30452518; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC6439832. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
