High-Minority Nursing Homes Disproportionately Affected by COVID-19 Deaths
- PMID: 33829006
- PMCID: PMC8019707
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.606364
High-Minority Nursing Homes Disproportionately Affected by COVID-19 Deaths
Abstract
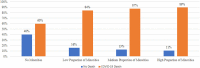
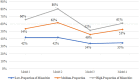
Racial/ethnic disparities in healthcare have been highlighted by the recent COVID-19 pandemic. Using the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services' Nursing Home COVID-19 Public File, this study examined the relationship between nursing home racial/ethnic mix and COVID-19 resident mortality. As of October 25, 2020, high minority nursing homes reported 6.5 COVID-19 deaths as compared to 2.6 deaths for nursing homes that had no racial/ethnic minorities. After controlling for interstate differences, facility-level resident characteristics, resource availability, and organizational characteristics, high-minority nursing homes had 61% more COVID-19 deaths [Incidence Rate Ratio (IRR) = 1.61; p < 0.001] as compared to nursing facilities with no minorities. From a policy perspective, nursing homes, that serve primarily minority populations, may need additional resources, such as, funding for staffing and personal protective equipment in the face of the pandemic. The COVID-19 pandemic has sharpened the focus on healthcare disparities and societal inequalities in the delivery of long-term care.
Keywords: COVID-19; disparities; mortality; nursing homes; race/ethnicity.
Copyright © 2021 Weech-Maldonado, Lord, Davlyatov, Ghiasi and Orewa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- KFF . State Data and Policy Actions to Address Coronavirus. Kaiser Family Foundation. Available online at: https://www.kff.org/health-costs/issue-brief/state-data-and-policy-actio... (accessed July 17, 2020).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

