Surprising Hyperkalemia of 10.2 mmol/L in a Patient with Hyperglycemia: A Case Report
- PMID: 33829044
- PMCID: PMC7991282
- DOI: 10.1159/000512590
Surprising Hyperkalemia of 10.2 mmol/L in a Patient with Hyperglycemia: A Case Report
Abstract
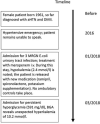
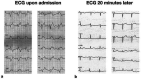
Hyperkalemia is a life-threatening condition potentially leading to cardiac arrest. Here, we report a case of surprising severe hyperkalemia of 10.2 mmol/L in a diabetic patient with previously normal kidney function presenting without discernible clinical symptoms to our emergency department. The patient was admitted because of hyperglycemia of 32.8 mmol/L, which was detected during daily testing in her nursing home. The hyperkalemia was caused by prerenal failure due to hyperglycemic polyuria which led to volume depletion, and worsened by a combination of potassium-sparing drugs and potassium supplementation. The patient was treated conservatively. Eighteen hours later, the serum potassium concentration was 4.6 mmol/L. The patient could be released 6 days later. To our knowledge, this is the highest described hyperkalemia treated conservatively and survived without cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Hyperglycemia; Hyperkalemia.
Copyright © 2021 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Skorecki K, Chertow GM, Marsden PA, Taal MW, Yu AS. Brenner & Rector's the kidney. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier; 2016.
-
- Hoppe LK, Muhlack DC, Koenig W, Carr PR, Brenner H, Schöttker B. Association of Abnormal Serum Potassium Levels with Arrhythmias and Cardiovascular Mortality: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018 Apr;32((2)):197–212. - PubMed
-
- te Dorsthorst RP, Hendrikse J, Vervoorn MT, van Weperen VY, van der Heyden MA. Review of case reports on hyperkalemia induced by dietary intake: not restricted to chronic kidney disease patients. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019;73((1)):38–45. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

