A Robotic Framework to Facilitate Sensory Experiences for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 33829148
- PMCID: PMC8023221
- DOI: 10.1145/3359613
A Robotic Framework to Facilitate Sensory Experiences for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
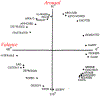
The diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children is commonly accompanied by a diagnosis of sensory processing disorders. Abnormalities are usually reported in multiple sensory processing domains, showing a higher prevalence of unusual responses, particularly to tactile, auditory and visual stimuli. This paper discusses a novel robot-based framework designed to target sensory difficulties faced by children with ASD in a controlled setting. The setup consists of a number of sensory stations, together with two different robotic agents that navigate the stations and interact with the stimuli. These stimuli are designed to resemble real world scenarios that form a common part of one's everyday experiences. Given the strong interest of children with ASD in technology in general and robots in particular, we attempt to utilize our robotic platform to demonstrate socially acceptable responses to the stimuli in an interactive, pedagogical setting that encourages the child's social, motor and vocal skills, while providing a diverse sensory experience. A preliminary user study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of the proposed framework, with a total of 18 participants (5 with ASD and 13 typically developing) between the ages of 4 and 12 years. We derive a measure of social engagement, based on which we evaluate the effectiveness of the robots and sensory stations in order to identify key design features that can improve social engagement in children.
Keywords: Human-robot interaction; autism spectrum disorder; sensory processing disorder; social engagement; socially assistive robots.
Figures

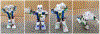

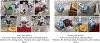


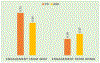

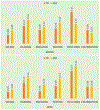

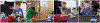
Similar articles
-
Improving therapeutic outcomes in autism spectrum disorders: Enhancing social communication and sensory processing through the use of interactive robots.J Psychiatr Res. 2017 Jul;90:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Feb 7. J Psychiatr Res. 2017. PMID: 28213292 Review.
-
A Music-Therapy Robotic Platform for Children With Autism: A Pilot Study.Front Robot AI. 2022 May 23;9:855819. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2022.855819. eCollection 2022. Front Robot AI. 2022. PMID: 35677082 Free PMC article.
-
Toward an Automated Measure of Social Engagement for Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder-A Personalized Computational Modeling Approach.Front Robot AI. 2020 Apr 15;7:43. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2020.00043. eCollection 2020. Front Robot AI. 2020. PMID: 33501211 Free PMC article.
-
Shared and Divergent Auditory and Tactile Processing in Children with Autism and Children with Sensory Processing Dysfunction Relative to Typically Developing Peers.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2015 Jul;21(6):444-54. doi: 10.1017/S1355617715000387. Epub 2015 Jul 6. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2015. PMID: 26145730
-
Building and testing of a robotic intervention framework to enhancing the social engagement of children with autism spectrum disorder.Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2025 May;20(4):878-888. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2024.2412076. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2025. PMID: 39378054 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Contextualized Affective Interactions With Robots.Front Psychol. 2021 Nov 2;12:780685. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.780685. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34795623 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Assistive technology for adults on the autism spectrum: A systematic survey.Int J Hum Comput Interact. 2024;40(10):2433-2452. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2022.2163568. Epub 2023 Jan 8. Int J Hum Comput Interact. 2024. PMID: 38784821 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral Data Analysis of Robot-Assisted Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Interventions Based on Lattice Computing Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 14;22(2):621. doi: 10.3390/s22020621. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062582 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting Social Engagement With a Multi-Role Dancing Robot for In-Home Autism Care.Front Robot AI. 2022 Jun 20;9:880691. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2022.880691. eCollection 2022. Front Robot AI. 2022. PMID: 36203792 Free PMC article.
-
Ethical Design of a Robot Platform for Disabled Employees: Some Practical Methodological Considerations.Front Robot AI. 2021 Aug 19;8:643160. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2021.643160. eCollection 2021. Front Robot AI. 2021. PMID: 34490354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grandin Temple. Thinking in pictures: And other reports from my life with autism. Vintage, 2006.
-
- Tomchek Scott D., and Dunn Winnie. "Sensory processing in children with and without autism: a comparative study using the short sensory profile." American Journal of occupational therapy 61, no. 2 (2007): 190–200. - PubMed
-
- Leekam Susan R., Nieto Carmen, Libby Sarah J., Wing Lorna, and Gould Judith. "Describing the sensory abnormalities of children and adults with autism." Journal of autism and developmental disorders 37, no. 5 (2007): 894–910. - PubMed
-
- Kern Janet K., Trivedi Madhukar H., Garver Carolyn R., Grannemann Bruce D., Andrews Alonzo A., Savla Jayshree S., Johnson Danny G., Mehta Jyutika A., and Schroeder Jennifer L.. "The pattern of sensory processing abnormalities in autism." Autism 10, no. 5 (2006): 480–494. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
