Treatment planning of volumetric modulated arc therapy and positioning optimization for hippocampal-avoidance prophylactic cranial irradiation
- PMID: 33829650
- PMCID: PMC8130238
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13217
Treatment planning of volumetric modulated arc therapy and positioning optimization for hippocampal-avoidance prophylactic cranial irradiation
Abstract
Background: Hippocampal-avoidance prophylactic cranial irradiation (HA-PCI) offers potential neurocognitive benefits but raises technical challenges to treatment planning. This study aims to improve the conventional planning method using volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) technique and investigate a better patient's head positioning to achieve a high quality of HA-PCI treatment plans.
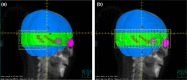
Methods: The improved planning method set a wide expansion of hippocampus as a special region for dose decline. The whole brain target was divided into two parts according to whether the slice included hippocampus and their optimization objectives were set separately. Four coplanar full arcs with partial field sizes were employed to deliver radiation dose to different parts of the target. The collimator angle for all arcs was 90°. Tilting patient's head was achieved by rotating CT images. The improved planning method and tilted head positioning were verified using datasets from 16 patients previously treated with HA-PCI using helical tomotherapy (HT).
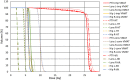
Results: For the improved VMAT plans, the max and mean doses to hippocampus were 7.88 Gy and 6.32 Gy, respectively, significantly lower than those for the conventional VMAT plans (P < 0.001). Meanwhile, the improved planning method significantly improved the plan quality. Compared to the HT plans, the improved VMAT plans result in similar mean dose to hippocampus (P > 0.1) but lower max dose (P < 0.02). Besides, the target coverage was the highest for the improved VMAT plans. The tilted head positioning further reduced the max and mean doses to hippocampus (P < 0.05), significantly decreased the max dose to lens (P < 0.001) and resulted in higher plan quality as compared to nontilted head positioning.
Conclusions: The improved planning method enables the VMAT plans to meet the clinical requirements of HA-PCI treatment with high plan quality and convenience. The tilted head positioning provides superior dosimetric advantages over the nontilted head positioning, which is recommended for clinical application.
Keywords: helical tomotherapy; hippocampus; prophylactic cranial irradiation; volumetric modulated arc therapy.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dosimetric comparison of helical tomotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy in hippocampal avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jan;25(1):e14218. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14218. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38013656 Free PMC article.
-
Current dilemma and future directions over prophylactic cranial irradiation in SCLC: a systematic review in MRI and immunotherapy era.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 30;14:1382220. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1382220. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39139283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intensity-modulated proton therapy for hippocampal-sparing prophylactic cranial irradiation: a planning comparison with photon therapy.BMC Cancer. 2025 Apr 8;25(1):639. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14039-6. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40200186 Free PMC article.
-
The Capabilities and Characteristics of Helical Tomotherapy and Co-Planar Dual Arcs Volumetric-Modulated arc Therapy Associated with Hippocampal Sparing During Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211043975. doi: 10.1177/15330338211043975. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34632869 Free PMC article.
-
Technical recommendations for implementation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy and Helical Tomotherapy Total Body Irradiation.Radiother Oncol. 2024 Aug;197:110366. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110366. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Radiother Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38830537 Review.
Cited by
-
Dosimetric comparison of helical tomotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy in hippocampal avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jan;25(1):e14218. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14218. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38013656 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal sparing in whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: controversy, technology and the future.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 24;14:1342669. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1342669. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38327749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current dilemma and future directions over prophylactic cranial irradiation in SCLC: a systematic review in MRI and immunotherapy era.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 30;14:1382220. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1382220. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39139283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of piecewise VMAT technique to whole-brain radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost for multiple metastases.Radiat Oncol. 2022 May 7;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02059-6. Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35526019 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing the optimized hippo-avoidance prophylactic cranial irradiation for limited-stage small cell lung cancer by tomotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy.Thorac Cancer. 2024 Dec;15(34):2449-2455. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15462. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Thorac Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39440477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slotman BJ, Faivre‐Finn C, Kramer G, et al, Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation (PCI) in Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (ES‐SCLC) (EORTC 22993–08993). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69:S4. - PubMed
-
- Slotman B, Faivre‐Finn C, Kramer G, et al, A randomized trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) versus no PCI in extensive disease small cell lung cancer after a response to chemotherapy (EORTC 08993–22993). J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4.
-
- Pöttgen C, Eberhardt W, Grannass A, et al, Prophylactic cranial irradiation in operable stage IIIA non‐small‐cell lung cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: results from a German multicenter randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4987–4992. - PubMed
-
- Stuschke M, Pöttgen C. Prophylactic cranial irradiation as a component of intensified initial treatment of locally advanced non‐small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2003;42:53–56. - PubMed
-
- Witlox W, Ramaekers B, Groen H, et al, The effect of prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) for young stage III NSCLC patients: Subgroup analyses of the NVALT‐11/DLCRG‐02 study. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:ii33–ii34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

