Correlation of humoral immune responses to different SARS-CoV-2 antigens with virus neutralizing antibodies and symptomatic severity in a German COVID-19 cohort
- PMID: 33830901
- PMCID: PMC8079054
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1913973
Correlation of humoral immune responses to different SARS-CoV-2 antigens with virus neutralizing antibodies and symptomatic severity in a German COVID-19 cohort
Abstract
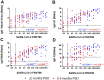
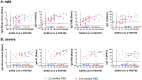
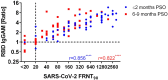
Monitoring the humoral protective immune response and its durability after SARS-CoV-2 infections is essential for risk assessment of reinfections, the improvement of diagnostic methods and the evaluation of vaccine trials. We have analyzed neutralizing antibodies and IgG responses specific to different antigens, including the inactivated whole-virion of SARS-CoV-2, the spike subunit 1 protein and its receptor binding domain, as well as the nucleocapsid protein. We show the dynamic developments of the responses from the early convalescent stages up to 9 months post symptoms onset in follow-up samples from 57 COVID-19 patients with varying clinical severity. By correlating antibody signals to neutralizing titres, valid diagnostic markers for the estimation of neutralizing protection could be identified.
Keywords: COVID-19; RBD-ELISA; S1-ELISA; humoral immunity; inactivated SARS-CoV-2; neutralizing antibodies; nucleocapsid-ELISA.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, et al. . A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. The Lancet [Internet]. 2020;395:470–473. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673620301859. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
