Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of late embryogenesis abundant protein-encoding genes in rye (Secale cereale L.)
- PMID: 33831102
- PMCID: PMC8031920
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249757
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of late embryogenesis abundant protein-encoding genes in rye (Secale cereale L.)
Abstract
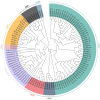
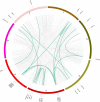
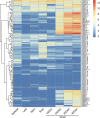
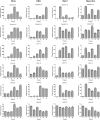
Late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins are members of a large and highly diverse family that play critical roles in protecting cells from abiotic stresses and maintaining plant growth and development. However, the identification and biological function of genes of Secale cereale LEA (ScLEA) have been rarely reported. In this study, we identified 112 ScLEA genes, which can be divided into eight groups and are evenly distributed on all rye chromosomes. Structure analysis revealed that members of the same group tend to be highly conserved. We identified 12 pairs of tandem duplication genes and 19 pairs of segmental duplication genes, which may be an expansion way of LEA gene family. Expression profiling analysis revealed obvious temporal and spatial specificity of ScLEA gene expression, with the highest expression levels observed in grains. According to the qRT-PCR analysis, selected ScLEA genes were regulated by various abiotic stresses, especially PEG treatment, decreased temperature, and blue light. Taken together, our results provide a reference for further functional analysis and potential utilization of the ScLEA genes in improving stress tolerance of crops.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


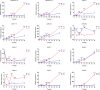
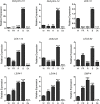
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of late embryogenesis abundant protein-encoding gene family in wheat: Evolution and expression profiles during development and stress.Gene. 2020 Apr 30;736:144422. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144422. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32007584
-
Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic and expression pattern analyses of EPF/EPFL family genes in the Rye (Secale cereale L.).BMC Genomics. 2024 May 30;25(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10425-9. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38816796 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of the LEA protein gene family in tea plant reveal their involvement in seed development and abiotic stress responses.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 1;9(1):14123. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50645-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31575979 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Stress-Responsive Expression Profiling of Genes Encoding LEA (Late Embryogenesis Abundant) Proteins in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis).PLoS One. 2016 Nov 9;11(11):e0165953. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165953. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27829056 Free PMC article.
-
The specificity and genetic background of the rye (Secale cereale L.) tissue culture response.Plant Cell Rep. 2013 Jan;32(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s00299-012-1342-9. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Plant Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23007688 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional in vitro diversity of an intrinsically disordered plant protein during freeze-thawing is encoded by its structural plasticity.Protein Sci. 2024 May;33(5):e4989. doi: 10.1002/pro.4989. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38659213 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Late Embryogenesis Abundant Protein Gene Family in Vigna Species and Expression of VrLEA Encoding Genes in Vigna glabrescens Reveal Its Role in Heat Tolerance.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 22;13:843107. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.843107. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35392521 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the BcLEA Gene Family and Functional Analysis of the BcLEA73 Gene in Wucai (Brassica campestris L.).Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 5;14(2):415. doi: 10.3390/genes14020415. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y, Li C, Zhang B, Yi J, Yang Y, Kong C, et al.. The role of the late embryogenesis-abundant (LEA) protein family in development and the abiotic stress response: a comprehensive expression analysis of potato (Solanum Tuberosum). Genes (Basel). 2019;10(2):148. 10.3390/genes10020148 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang XS, Zhu HB, Jin GL, Liu HL, Wu WR, Zhu J. Genome-scale identification and analysis of LEA genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci. 2007;172(2):414–420. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.10.004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

