SARS-CoV-2 evolution in an immunocompromised host reveals shared neutralization escape mechanisms
- PMID: 33831372
- PMCID: PMC7962548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.027
SARS-CoV-2 evolution in an immunocompromised host reveals shared neutralization escape mechanisms
Abstract
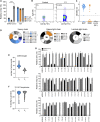
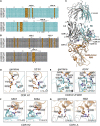
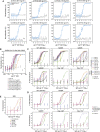
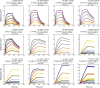
Many individuals mount nearly identical antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2. To gain insight into how the viral spike (S) protein receptor-binding domain (RBD) might evolve in response to common antibody responses, we studied mutations occurring during virus evolution in a persistently infected immunocompromised individual. We use antibody Fab/RBD structures to predict, and pseudotypes to confirm, that mutations found in late-stage evolved S variants confer resistance to a common class of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies we isolated from a healthy COVID-19 convalescent donor. Resistance extends to the polyclonal serum immunoglobulins of four out of four healthy convalescent donors we tested and to monoclonal antibodies in clinical use. We further show that affinity maturation is unimportant for wild-type virus neutralization but is critical to neutralization breadth. Because the mutations we studied foreshadowed emerging variants that are now circulating across the globe, our results have implications to the long-term efficacy of S-directed countermeasures.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; affinity maturation; antibody neutralization; immunocompromised host; neutralization escape; variants of concern.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest A provisional application protecting various aspects of inventions described in this publication has been filed by the President and Fellows of Harvard University.
Figures


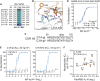


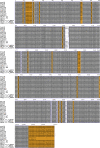
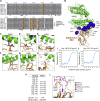
Update of
-
Molecular basis for a germline-biased neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Nov 13:2020.11.13.381533. doi: 10.1101/2020.11.13.381533. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell. 2021 May 13;184(10):2605-2617.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.027. PMID: 33200128 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Aricescu A.R., Lu W., Jones E.Y. A time- and cost-efficient system for high-level protein production in mammalian cells. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2006;62:1243–1250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

