In silico analysis of the potential mechanism of a preventive Chinese medicine formula on coronavirus disease 2019
- PMID: 33831468
- PMCID: PMC8020622
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114098
In silico analysis of the potential mechanism of a preventive Chinese medicine formula on coronavirus disease 2019
Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance: With the spread of Coronavirus Disease (2019) (COVID-19), combination with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been widely used as a prevention and therapy strategy in China. Xin guan No.1 (XG-1) prescription is a preventive formula recommended by the Hunan Provincial Administration of TCM to prevent the pandemic of COVID-19.
Aim of the study: To explore the potential preventive mechanisms of XG-1 against COVID-19 in the combination of network pharmacology approach, single-cell RNA expression profiling analysis, molecular docking and retrospective study.
Materials and methods: Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine (ETCM) database was used to determine the meridian tropism, active components and target genes of XG-1. Gene ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) functional enrichment analysis were conducted by R Cluster Profiler package (3.14.3). Single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data of human lung (GSE122960) was downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and analyzed by R Seurat package (3.1.2). Cytoscape (3.7.2) was used to construct the interaction network. The main ingredients in XG-1 were identified by HPLC- Q-TOF- MS and used for molecular docking with COVID-19 3CL hydrolytic enzyme and angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2). A retrospective study of 47 close contact participants from Dongtang Community of Hunan Province was conducted to evaluated the preventive effect of XG-1.
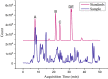
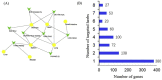
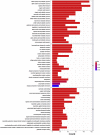
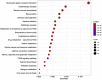
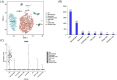
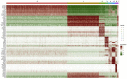
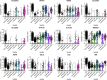
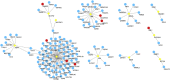
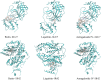
Results: According to the network pharmacology analysis, XG-1 formula was closely related to lung-, spleen- and stomach-meridians and include a total of 206 active components and 853 target genes. GO and KEGG pathway enrichment revealed that XG-1 mainly regulated cellular amino acid metabolism process and neuroactive ligand-receptors interaction. The scRNA-seq profiling showed that angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) was principally expressed in alveolar type 2 epithelial cells (AT2). 153 genes were up-regulated in AT2 cells expressing ACE2 and 12 genes were obtained by intersecting with XG-1 target genes, of which 3 were related to immunity. Five main chemical ingredients were detected in XG-1 sample by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS. The molecular docking showed that Rutin, Liquiritin and Astragaloside Ⅳ had a good affinity with COVID-19 3CL hydrolytic enzyme and ACE2. Compared with participants who didn't take XG-1, preventive treatment with XG-1gradules resulted in a significant lower rate of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid (P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: The present study showed that XG-1 exerts a preventive effect in close contacts against COVID-19. The underlying mechanism may be related to modulate immunity response through multiple components, pathways, and several target genes co-expressed with ACE2. These findings provide preliminary evidences and methodological reference for the potential preventive mechanism of XG-1 against COVID-19.
Keywords: Chinese medicine preventive formula; Close contacts; Coronavirus disease 2019; Molecular docking; Network pharmacology; Single-cell RNA Sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bi Q., Wu Y., Mei S., Ye C., Zou X., Zhang Z., Liu X., Wei L., Truelove S.A., Zhang T., Gao W., Cheng C., Tang X., Wu X., Wu Y., Sun B., Huang S., Sun Y., Zhang J., Ma T., Lessler J., Feng T. Epidemiology and transmission of COVID-19 in 391 cases and 1286 of their close contacts in Shenzhen, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020;20(8):911–919. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30287-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- General Office of the National Health Commission . 2020. Diagnosis and Treatment Plan for COVID-19 (Trial Version 8)http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-08/19/5535757/files/da89edf7cc9...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

